China keen to be part of African dream
|
 |
|
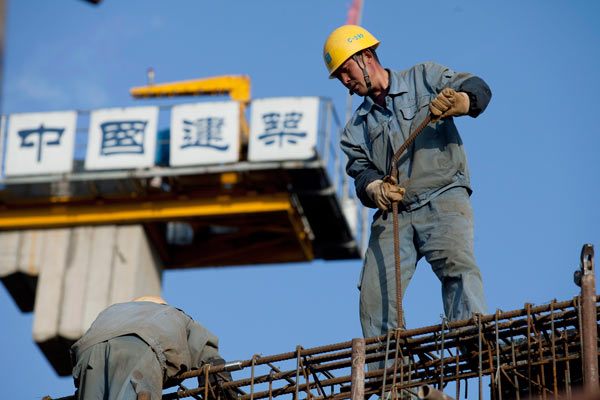
The African Union Conference Center in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, which was under construction in this photo dated Jan 28, 2010, is one of the infrastructure projects that China has helped build in Africa. MAO SIQIAN / XINHUA |
While Chinese aid and investment in Africa have largely focused on infrastructure construction work to facilitate the development of African countries, critics have complained that China is only interested in building roads to areas that boast rich natural resources.
However, Chinese construction companies are participating in the construction of a trans-continental transport network to help fulfill the aspirations of pan-Africanists.
"If we seek to develop our continent, then we need the involvement of China," said Elham Ibrahim, commissioner for infrastructure and energy of the African Union Commission. "Especially in my area, infrastructure and energy industry, China should, and could, play a big role."
The Horn of Africa is eager for a trans-border road that would connect Addis Ababa and Nairobi. The road would be part of a larger plan to link Alexandria in Egypt in the north of the continent with Cape Town in South Africa, and Chinese construction companies are working hard to build the road.
"The A2 highway project is designed to connect the two most important cities in the horn region," said Liu Hui, chairman of the construction company China Wuyi Kenya Co. "The project has been divided into several sections; my company has finished one part and is now taking over work on another section, from Turbi to Moyale, on the border of Ethiopia and Kenya."
Having worked on infrastructure projects in Africa for more than a decade and witnessed the development of the continent, Liu said African countries have differing levels of development, which means the infrastructure conditions vary as well.
"Roads and railways are essential to fill the gap and facilitate the market and communications between countries," he said. "Once connected, human and natural resources and trade will begin to flow."
Construction of the 7-meter-wide, 129.63-km-long road will take around 36 months, but the company will also be responsible for its maintenance for a further two years.
The project cuts through some of the toughest conditions in Kenya, the Gobi region in the north of the country. "Ours is the hardest part of the entire project, because there is no water, no usable soil and no logistics supplement," said Li Shoujie, deputy director of Jiangxi Zhongmei Engineering Construction (Kenya) Co.
"People tried to build a road, but were daunted by the harsh environment. However, the main virtues of Chinese companies are hard work and endurance, so we have to make this vision come true," he said.
"There was once a road in this region and on this route, but it was too poor to be convenient or efficient, so it was really just a nominal road on the map," he added.
"Infrastructure and energy serve the most fundamental and basic roles in establishing a more integrated and united Africa," said the AUC's Ibrahim. "Without infrastructure, we will not be able to achieve the objectives set by African countries."
She said that connecting people is the most important factor in facilitating regional and continental integration, through improved transport links and telecommunications, so people can meet and work together.
As China already boasts a number of successful large-scale construction projects, the country has proved its ability to build transnational projects in Africa.
"We have the nine corridors of the Trans-Africa Highway, including highways from Cairo to Cape Town and Algeria to Lagos. Now we are trying to complete these projects, which began several decades ago. Admittedly, there are still many missing links and some of them need to be rehabilitated or upgraded to meet the standards of international highways," said Ibrahim.
However, finance remains a problem, one that requires the support of the international community. Thus China's future aid and investment in infrastructure construction, especially transportation networks, will be vital to Africa's successful integration, she said.
|
 |
|
This 2010 photo shows Chinese workers on the African Union Building in Addis Ababa. PROVIDED TO CHINA DAILY
|
"Africa has so many countries but inter-nation trade still remains at a low level and the market is small. However, this doesn't suggest there is no need for greater communication, on the contrary, it indicates great potential," said Yao Guimei, a researcher at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences' Research Institute for West Asian and North African Affairs.
"The Chinese government is encouraging its companies and financial institutions to join this process, to join bilateral or multilateral projects," she added. "Some of the companies have chosen pivotal African cities as bases from which they can radiate to other places."
Integration is a life or death choice for Africa in terms of sustainable and rapid economic growth, according to Rene N'Guettia Kouassi, the AUC's director of economic affairs.
"Despite the global financial crisis, the African economy is in a good position. A lot has been done, but a lot remains to be done to achieve our goal, which is to build a 'State of Africa'," he said.
Under such a state, the continent would have a common currency and financial institutions such as a pan-African Bank, an African Monetary Fund and an African Stock Exchange.
The European Union implemented a common currency 13 years ago, which resulted in a deepening of economic integration among member countries. However, the ongoing sovereign debt crisis has now pushed several countries to the edge of bankruptcy.
"Africa will definitely learn the lessons of the EU and elsewhere to make our integration safer and more efficient," said Kouassi. "In Africa, we are undertaking two crucial tasks, economic integration and political integration, which move in parallel."
No individual country is strong enough to face the global challenges alone, so Africa has to unite its strengths. Regional organizations such as the Economic Community of West African States, the East African Community and the Southern African Development Community serve as good examples of this, he said.
"They are implementing a single customs union, which means free movement of goods between countries and a single external tax for imports, which is convenient and attractive to foreign investors."
The AU is at the forefront of a plan to set up an African common market and customs union by 2019, he said. "An integrated Africa will be good for the outside world, including China, because there will be a common market with a common currency. The market will be there for investment from all investors and will be more convenient."
China has a large role to play in this process, he said, but urged greater understanding of the problems, such as the need for infrastructure development.
"The fruits of development and growth are not shared efficiently and may not reach the poor, so when China provides assistance, we should pay more attention to things such as this," he said.