When an only child dies, hope evaporates
By Shan Juan (China Daily) Updated: 2014-04-10 07:17
|
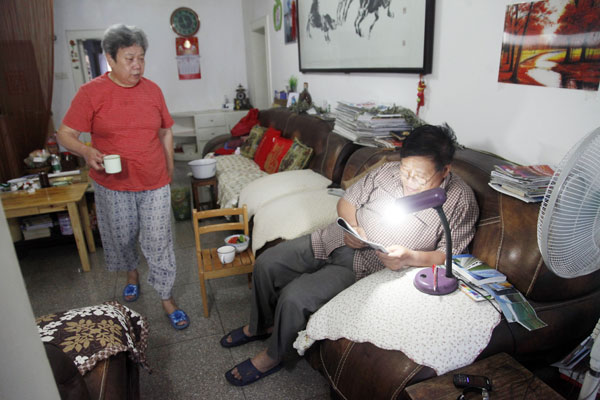 |
| Hu Dehua, 67, and her husband Chen Fang at their home in Changsha, Hunan province. The couple lost their son through illness in June 2011. FU ZHIYONG / FOR CHINA DAILY |
Project explores ways to provide care and support for parents whose child has predeceased them, reports Shan Juan
After six months of self-imposed seclusion following the unexpected death of her son, Zhang Liying was determined to muster the courage to have another child.
|
Beijing boosts bereaved parents
More than 8,000 bereaved parents in Beijing have joined a free insurance program to help relieve the financial burden as they grow older and become susceptible to illness and accidents. The Warm Heart Plan was launched on June 15, 2012, after the Beijing Family Planning Association signed an agreement with an insurance company in December 2011. The city government will provide bereaved parents with a special monthly subsidy of 200 yuan ($32) per person. The plan, which the government will purchase annually for three years, pays for medical fees incurred as a result of accidents and also provides cover for beneficiaries if the policyholders die of illness or accident. Women diagnosed with gynecological cancers will receive a minimum one-time payment of 2,000 yuan. People aged 55 or older will also receive a maximum one-time pension payment of 8,700 yuan. In 2012-13, the city government paid 2.16 million yuan to buy insurance cover for 7,746 bereaved parents. In 2013, it paid 24.49 million yuan to allow 8,781 bereaved parents to join the plan. The plan will be reviewed in June 2015 to decide whether to continue with it, according to the BFPA. Hao Yansu, dean of the School of Insurance at the Central University of Finance and Economics, welcomed the plan as a good example for other provinces and cities. "The insurance plan complements the government subsidy paid to bereaved parents who followed the national policy by only having one child," he said. "Instead of including it in the public insurance program and administering the plan itself, the government purchased the cover from an insurance company. Therefore, it can supervise operations more strictly by publicly monitoring the company." Hao said that the plan can, and should, become a sustainable policy for bereaved parents nationwide. - Wang Qingyun |
"We need to move on, and a child is necessary for my life," said the 40-year-old from the Baqiao district of Xi'an, Shaanxi province, whose son drowned in 2012 at the age of 20.
Life went into suspended animation from that moment. "I saw no reason to live on. I felt ashamed at losing my son and thought it must be my fault," she said.
However, Zhang gradually became more optimistic after she was approached by family planning workers who offered care and support, including peer-support activities, mental health intervention and a free course of assisted reproductive technology.
"Without government help, a farming family like us couldn't afford the treatment, which costs about 50,000 yuan ($8,000)," she said.
Zhang and her husband are not alone, according to Jia Wenying, head of the Baqiao family planning bureau, who said 137 couples in the district have lost their only child through illness or accident.
Factory worker Hua Jie said she cried so much when her depressed daughter committed suicide at the age of 26 that her eyesight was affected. "I put away all her photos but couldn't help sobbing when I saw other women of a similar age to my daughter," said the 58-year-old.
To some extent, Hua has been fortunate: Following their daughter's death, her husband refused to bow to grief and tried to remain positive and optimistic, said Ding Baorong, a bureau worker who has provided care for more than 100 bereaved families.
In many cases, bereaved couples blame each other for their loss. That makes the marriage unsustainable and usually results in divorce.
With a combined monthly wage of about 4,000 yuan ($645), Hua and her husband, surnamed Feng, enjoy a relatively comfortable life, but they are apprehensive about the future. "We are concerned about when we get old and can't take care of ourselves," said Feng. "By that time, our wages won't even pay for two beds at a decent rest home in Xi'an. I hope the government will help us if that happens."
They have never linked their personal tragedy with China's family planning policy, which was introduced in the late 1970s and limited most couples to just one child. "But given the opportunity, I would certainly have had more than one child," said Hua.
According to Jia, nearly 50 percent of bereaved one-child couples in Baqiao district are urbanites aged between 50 and 60.
"They are more in need of mental consolation than financial support," she said, citing a 2012 survey conducted by the China Family Planning Association as part of a three-year project to explore models of care and support for parents whose only child has predeceased them.
To date, more than 70 regions nationwide have participated in the project. Each region receives an annual care-and-support subsidy of 200,000 yuan on condition the local government provides an equal amount, according to Yang Yuxue, executive deputy director of the association.
"The project was designed as a catalyst to encourage local governments to provide long-term, sustainable care for bereaved parents," he said.
A valuable lesson
Ding devised a questionnaire to accompany the survey. It contained more than 20 questions - including basic information about economic situation, marital status and the couple's emotional state - designed to help carers understand the plight of bereaved parents and cater to their needs.
However, some parents saw the questionnaire as an unwarranted intrusion into private grief. "One woman called Ni, who lost her 20-year-old daughter to bone cancer and subsequently divorced, turned us away from her door when we tried to give her the questionnaire. She taught us a valuable lesson and prompted changes in the way we work with bereaved parents. We understood that we had to listen more and be more respectful," Ding said.
- More female officials caught in corruption
- Whampoa veterans recorded with glory
- Police bust 9 terrorist groups in Xinjiang
- Knife-wielding attackers seized in Xinjiang
- New regulation leads to drop in petitioned cases
- Hunan plant shut as probe into lead poisoning begins
- Police boost efforts to combat gambling
- Project offers jobs openings to legal experts
- Experts: Dog meat festival 'illegal'
- Nation looks to upgrade
pipeline networks