Meeting mummy in the valley of the giants
By Cui Jia and Gao Bo (China Daily) Updated: 2014-05-14 07:32The human museum
Xinjiang is known for its dry climate and sandy landforms, resulting in ancient corpses dehydrating quickly and mummifying, so the region is a museum of the human race, according to Tian Weijiang, a researcher at the Xinjiang Academy of Social Sciences.
"Archaeological evidence indicates that human beings from different races have lived in Xinjiang since prehistoric times because of the area's location on the border of Central Asia. In the Xiaohe tomb, we found the remains of ancient Europeans and Mongolians," he said.
Xu Dongliang, deputy head of the Technological Protection Institute at the Academy of Turpan Studies, said the combination of low rainfall, high temperatures and arid air was a key element in the preservation of relics in Turpan prefecture, especially tombs and mummies.
Xu, 42, had recently returned from Changchun in Jilin province, where more than 170 ancient mummies unearthed in Turpan were being studied at Jilin University, which has one of China's leading molecular archaeology labs, as part of the first major study into physical anthropology, or behavioral and biological variation, in Xinjiang.
The mummies - children, adolescents, middle-aged and elderly people thought to have lived 2,500 to 3,000 years ago - were excavated from the Shengjindian tomb complex in Shengjin township and the Jiayi tomb complex in Yar township.
Experts at Jilin University's Research Center for Chinese Frontier Archaeology will use modern technology, including DNA detection, geological and pathological tests, to analyze the samples and provide archaeologists with more information.
Xu said the mummies were buried in different types of tombs, and the research will throw more light on the migratory habits and lifestyles of these ancient nomads and the relations between different races.
|
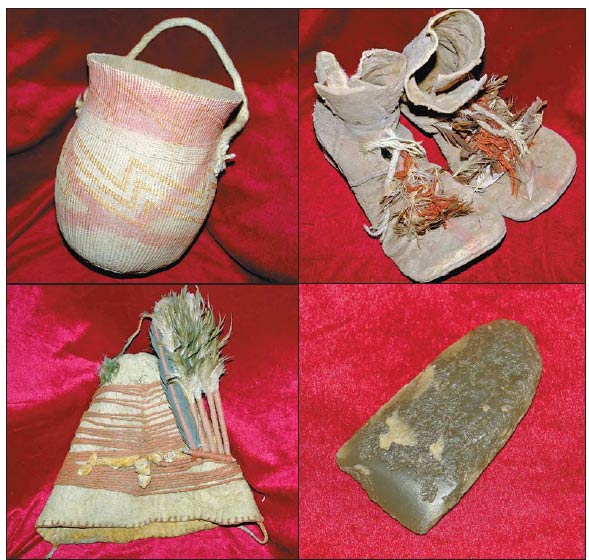 |
| Clockwise from top: Items found at the Kungang tomb, including a basket made of straw, a pair of leather boots, a jade axe and a felt hat. Experts say the tomb could date back 4,600 years. PHOTOS PROVIDED TO CHINA DAILY |
| More pictures about Kungang tomb |
Earliest wooden leg?
For example, earlier research on the mummy of a middle-aged man from about 2,300 years ago revealed that he had been fitted with a prosthetic leg more than 100 years before the Roman Capua Leg, one of the earliest-known prosthetic limbs.
"Making discoveries about the tombs and the mummies is also a process of understanding the history of Xinjiang and its people," Xu said. "Seeds excavated from the Supeixi tomb complex in 2003 show that grapes have been planted in Turpan for more than 2,500 years. The fruit is still the prefecture's specialty."
Xinjiang is extremely rich in archaeological relics, but lacks the high-tech research equipment and expertise needed for authoritative studies. Also, preserving mummies or the remains of ancient kingdoms in deserts is a difficult task, Xu said.
"The vast deserts in Xin-jiang have helped to preserve the historical relics, but they also make the sites difficult to maintain once excavation work begins because the sand dunes shift with the winds," he added.
Despite the challenges, the future of the preservation and study of archaeological discoveries in Xinjiang is still promising. "Many institutes are interested in our resources and have offered help. Jilin University will set up a station in Turpan and dispatch researchers with mobile equipment. That will reduce the influence of environmental changes and transport (from Xinjiang to Jilin) if we want to conduct tests," Xu said, adding that his team will conduct research into mummified animals in the near future.
Xu's laboratory is currently restoring silks discovered in an ancient tomb. "Every detail of the restoration work requires careful planning because the desert has made the fabric extremely fragile and it could easily break into pieces just at a touch, so we always take great care of these priceless artifacts," he said.
Contact the writers at cuijia@chinadaily.com.cn and gaobo@chinadaily.com.cn
- More female officials caught in corruption
- Whampoa veterans recorded with glory
- Police bust 9 terrorist groups in Xinjiang
- Knife-wielding attackers seized in Xinjiang
- New regulation leads to drop in petitioned cases
- Hunan plant shut as probe into lead poisoning begins
- Police boost efforts to combat gambling
- Project offers jobs openings to legal experts
- Experts: Dog meat festival 'illegal'
- Nation looks to upgrade
pipeline networks