|
|
 |
|
30th Anniversary Celebrations
Economic Development
New Rural Reform Efforts
Political System Reform
Changing Lifestyle
In Foreigners' Eyes
Commentary
Enterprise Stories
Newsmakers
Photo Gallery
Video and Audio
Wang Wenlan Gallery
Slideshow
Key Meetings
Key Reform Theories
Development Blueprint
Li Xing:
Teachers like Li need our support Alexis Hooi:
Going green in tough times Hong Liang:
Bold plan best option for economy Achin' to make bacon
By You Nuo (China Daily)
Updated: 2008-05-12 17:15
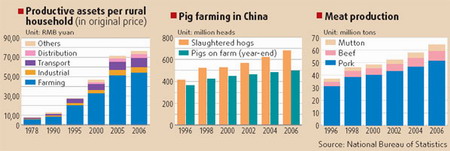
  For more than 2,000 years, the China's heartland (south of the Great Wall) has not seen traveling herdsmen on horseback, as in the northern grasslands, where the land in the Yangtze and Yellow valleys have been entirely used for intensive farming. The predominant way to produce meat has been through household-based pig farming. But not just for family consumption. The most important use for raising one or two hogs used to be for their owners to sell them to the urban slaughter houses in order to finance the farming operations and to buy daily necessities. During the reform era, for many rural households the first pieces of farm machinery were earned by selling pigs. Indeed, the poorer a place was, the more its members had to depend on pig farming for any little change in their lives - even though selling a hog could be a great trouble, as our photographer has shown here from a picture he took on a reporting tour in the early 1980s of a farmer carrying his hog to a township fair from his mountainous village in Hubei province. It was commonplace in the Chinese countryside in those days. Except for a few urban pockets, most of China was still rural, and most of the residents were struggling hard just to feed themselves. Having a hog to sell might be just the one thing that could lift them from the subsistence level. Today, while the nation's demand for meat has been rising, at least a fair number of farmers have found other ways to make a cash income. Carrying hogs to the township fair is no longer the only way for rural households to generate cash, as funds from young men and women working in the cities has become a more convenient way help to their relatives in their home villages. From mid-1990s to 2006, their spending on productive assets, mainly farm machinery, had grew more than 170 percent, while the country's pork production, including that from large State-run farms, rose by 60 percent. At the same time, pig farming has become more dependent on feed supplies, and has been concentrated in just a few provinces, such as Shandong, Hunan, and Sichuan and bearing an increasing resemblance to an industry. In another 30 years, one can reasonably imagine pigs will disappear from most Chinese households - except, however, those being kept as pets. One of the nation's pioneering pet pigs was also caught by our photographer's lens, this time in Beijing's 798 Complex, a renovated industrial neighborhood for the city's modern artists and art dealers. How time flies, you may say. And so do pigs.
 
 |