EyeSmart exploits biz potential in iris
 |
|
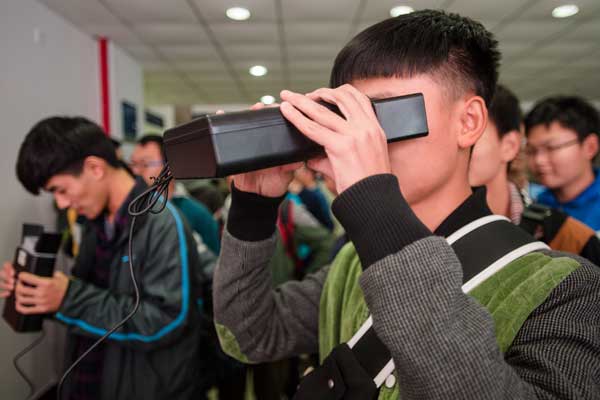
Freshmen at the Guilin University of Electronic Technology use EyeSmart devices to offer their iris data for their personal identity files. [Photo provided to China Daily] |
EyeSmart Technology Ltd, a Beijing-based startup, has applied biometric iris recognition technology to finance, education, public security, social security, healthcare and public welfare.
Iris recognition is a method of identifying people based on unique patterns within the ring-shaped region surrounding the pupil. As the iris of each person is unique and doesn't degenerate over time, forgery and identity theft are difficult, according to EyeSmart.
Wang Xiaopeng, founder of EyeSmart, said: "Compared with facial and fingerprint recognition, the error rate of iris recognition is much lower. Iris recognition is the most stable, accurate and safest biometric identification technology at present."
With the development of new technology, the requirement for information security is becoming increasingly high. Iris recognition has become valuable in national security, military security, public safety and personal information security.
Wang said EyeSmart's iris recognition technology does not require users to stand close to the machine as the hardware is able to identify someone six meters away and even if they are moving.
"Traditional fingerprint and facial recognition have some potential risks. For instance, people could undergo plastic surgery and fingerprints are easy to copy," said Wang.
He added the iris recognition technology does not require a card, password or physical contact whether it is for making contactless payment, using the tech in a smart home or a smart car.
Founded in 2010, EyeSmart now provides specialized iris recognition products and solutions for hi-tech companies. Its products are used at banks, airports and hospitals.
In December 2014, it launched the world's first iris phone. Users are able to unlock the phone or log in and even encrypt files by iris.
It also participated in India's national biometric identification system, providing key technology support.
In September 2010, India launched the biometric identification system, and collected data of residents, stored it and issued a 12-digit unique identification number called Aadhaar to each resident of India.
The Unique Identification Authority of India is responsible for the project, while EyeSmart worked on the project and finished the task of collecting the iris information of 1.2 billion people in India in 2016.
 |
|
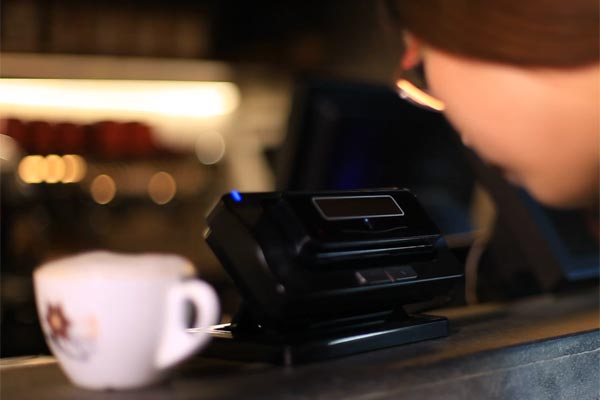
A customer pays a bill at a cafe using EyeSmart's iris recognition technology in Beijing. [Photo provided to China Daily] |
"In the next few years, we will provide various identity-based authentication solutions with certification companies in India for residents, which include certificates of bank transfer, consumption, payments, loans, salary payments and medical insurance," said Wang.
"Indian residents could enjoy digital medical services, social security, training, employment and online payment. The Indian government can also issue a subsidy and an allowance for targeted residents and monitor their health conditions."
Iris recognition technology has also been used in smartphones. Samsung Electronics Co Ltd launched its latest big-screen smartphone the Galaxy Note 7 with a curved screen and iris-recognition technology in August, but it was forced to recall the phones due to battery problem.
American professional rating organization IBG said the iris recognition market is growing at 30 percent a year, and the market value will reach more than $10 billion in the next five years.
Sun Zhenan, a researcher at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said iris recognition technology is definitely safer than face recognition and fingerprint recognition, but glass eyes and contact lenses could affect the process.
Contact the writers at fanfeifei@chinadaily.com.cn and zhoulihua@chinadaily.com.cn