A History of Tobacco in China
(chinadaily.com.cn) Updated: 2014-01-13 11:23China's anti-smoking movement was first recorded in 1639, when Ming Dynasty (AD 1368-1644) Emperor Chongzhen issued a national ban on tobacco and stipulated that tobacco addicts be executed. In 1637, Qing Dynasty (AD 1644–1911) Emperor Kangxi expanded the death penalty to those who possess tobacco.
 |
|
Qing Dynasty (AD 1644–1911) Emperor Kang Xi. [Photo/xinhuanet.com.cn] |
In 1817, the British began to sell a narcotic drug, Indian opium, to China as a way to reduce the trade deficit and to make the Indian colony profitable. The Qing Administration originally tolerated opium importation because it created an indirect tax on Chinese subjects, while allowing the British to double tea exports from China to England. However, by 1820 the planting of tea in the Indian and African colonies, along with accelerated opium consumption, reversed the flow of silver, and the drug had poisoned thousands of Chinese civilians.
 |
|
Photograph of two opium eaters in Qing Dynasty (AD 1644–1911). [Photo/tobaccochina.com] |
In 1839, the Daoguang Emperor appointed Lin Zexu Governor of Guangdong province to reduce and eliminate the opium trade. On his arrival at Guangzhou, Lin banned the sale of opium, demanded that all opium be surrendered to the Chinese authorities, and required that all foreign traders sign a "no opium trade" bond. Overall 20,000 chests (each holding about 55 kilograms) were handed over and destroyed in a 23-day campaign beginning June 3, 1839.
 |
|
Wax statues of Lin Zexu (right) and Qing Dynasty (AD 1644–1911) Emperor Daoguang in Fuzhou city of Fujian province on May 23, 2013. [Photo/icpress.cn] |
Although tobacco was consumed in China as early as the 1500s, cigarettes didn't arrive until the late 1800s, according to the archives at the US's Duke University, immediately after the invention of the cigarette machine in 1881, James B. Duke (1865—1925) is reported to have leafed through a world atlas to survey the population of foreign countries. Coming to the figure 430,000,000, he exclaimed, "That is where we are going to sell cigarettes." The country was China, and in 1890 the Dukes exported the first cigarettes to the populous Asian nation.
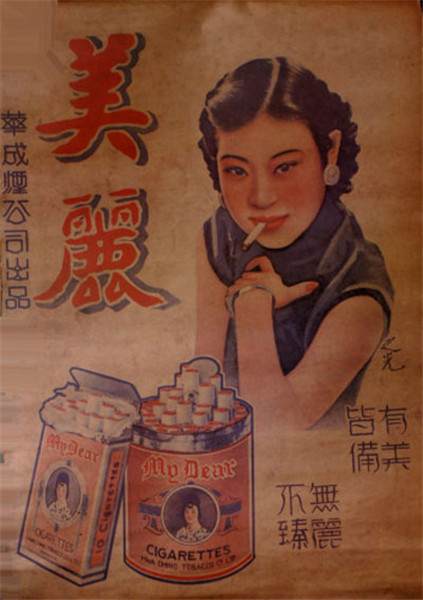
Advertisements featuring fashionable courtesans, or sing-song girls of Shanghai around the 1920s testified that the imported habit was trendy in what was then one of Asia's biggest cities.
 |
|
An advertisement for Shanghai's Meili brand cigarettes in the 1920s.[Photo/tobaccochina.com] |
In April 1935, the Kuomintang Party that then governed China issued a decree that aimed to eliminate drugs in two years and cigarettes in six years. Chiang Kai-shek, the party head, reformed the anti-drug commission under military departments to an independent section in charge of smoking elimination in the nation, and personnally took command.
Since the founding of People's Republic of China in 1949, the new Chinese government launched a vigorous crackdown on drugs and tobacco. 369,705 people involved in drug making, trafficking and selling were detected and punished. Farmlands were inspected to eliminate opium poppies.
A opium pipe confiscated during 1950s is on display at Shanghai Museum of Public Security in this undated photo. [Photo/bwg.police.sh.cn]

Although civilians were banned from the puff of pleasure, China's top leaders in the older generation took up the practice with gusto. Mao Zedong was often pictured with a cigarette in his hand, as in this 1957 shot of him meeting deputies from the Third National Congress of Chinese Communist Youth League.
 |
|
The chairman and his cigarette lighting fans, 1957. [Photo/xinhuanet.com.cn] |
Mao's successor Deng Xiaoping, another chain smoker, loved expensive Panda cigarettes, and often proffered them to visiting dignitaries. Here he speaks with former US Secretary of State Henry Kissinger, while preparing to light up:
 |
|
US Secretary of State Henry Kissinger in conversation with Deng Xiaoping. [Photo/xinhuanet.com.cn] |
- More female officials caught in corruption
- Whampoa veterans recorded with glory
- Police bust 9 terrorist groups in Xinjiang
- Knife-wielding attackers seized in Xinjiang
- New regulation leads to drop in petitioned cases
- Hunan plant shut as probe into lead poisoning begins
- Police boost efforts to combat gambling
- Project offers jobs openings to legal experts
- Experts: Dog meat festival 'illegal'
- Nation looks to upgrade
pipeline networks