China's unmanned lunar orbiter returns home
(Xinhua) Updated: 2014-11-01 09:18
|
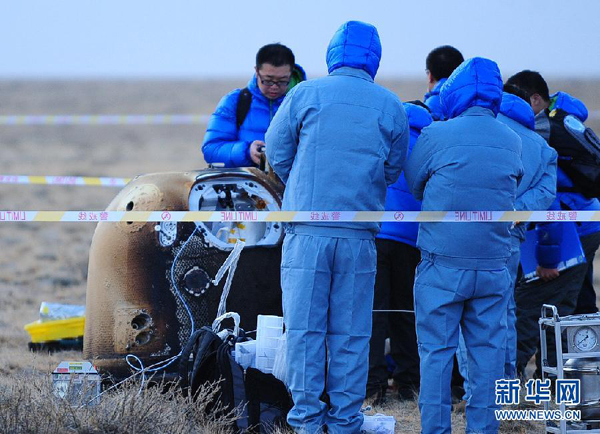 |
| Researchers retrieve the return capsule of China's unmanned lunar orbiter in the central region of North China's Inner Mongolia autonomous region, Nov 1, 2014. [Photo/xinhuanet.com] |
Earlier reports said Chang'e-5 will be launched around 2017. The goal is to collect samples from the Moon and return to Earth. If successful, China will become the third nation to do so.
Calling "Xiaofei" a pathfinder for Chang'e-5, Zhou Jianliang said the data acquired by the lunar orbiter will optimize technology for Chang'e-5.
Hao Xifan, deputy chief of China's third phase lunar exploration program, also said the mission validated ground support capacities, craft landing technology and recoverable spacecraft technology.
According to Wu Weiren, chief designer of China's lunar exploration program, Chang'e-5 is expected to collect a 2-kg sample from two meters under the Moon's surface and bring it home.
Aside from the high-speed re-entry, major technological challenges for the craft center on surface sampling, taking off from the Moon, and lunar orbit rendezvous, Wu said.
READY TO MAKE HISTORY, AGAIN
China launched a pair of orbiting lunar probes and last year landed a craft on the moon with a rover on board.
Saturday's success is another step forward for China's ambition that could eventually land a Chinese citizen there. Few countries can rival China's space program although China never intended to participate in any "space race".
In an earlier interview with Xinhua, Wu Weiren said lunar probe technology and software could be of great economic value if adapted for commercial use.
Commercial gains aside, the space program is already a marker of China's global stature and technical expertise. The Chang'e lunar probes - named after a goddess who took her pet Yutu, or jade rabbit, to the moon - are a symbol of great national pride.
The country sent its first astronaut into space in 2003, becoming the third nation after Russia and the U.S. to achieve manned space travel independently. In 2008, astronauts aboard the Shenzhou-7 made China's first space walk. There are plans for a permanent space station, expected to be set up around 2022.
The Chang'e-1 and Chang'e-2 missions in 2007 and 2010 respectively, capped the orbital phase of the three step project. Chang'e-1 crashed onto the Moon's surface at the end of its mission, and Chang'e-2 was sent into deep space to become China's first man-made asteroid.
The ongoing second phase saw Chang'e-3 soft land on the moon carrying moon rover Yutu in December 2013. Chang'e-4 was a backup for Chang'e-3 and has not been deployed.
In the meantime, Yutu has entered its 11th dormancy earlier October, although its functions have degraded considerably after it encountered control issues in January this year. Experts had feared that it might never function again, but Yutu has stubbornly managed to wake up from its sleep mode ever since.
None of those missions were intended to return to Earth and this has pushed the 2017 mission further into spotlight.
"The Chang'e-5 mission will be yet another historic moment for China's lunar program," Wu said.
- Govt encourages people to work 4.5 days a week
- Action to be taken as HIV cases among students rise
- Debate grows over reproductive rights
- Country's first bishop ordained in 3 years
- China builds Tibetan Buddhism academy in Chengdu
- Authorities require reporting of HIV infections at schools
- Typhoon Soudelor kills 14 in East China
- Police crack down on overseas gambling site
- Debate over death penalty for child traffickers goes on
- Beijing to tighten mail security for war anniversary