Expert makes new findings on history of papermaking
 |
|
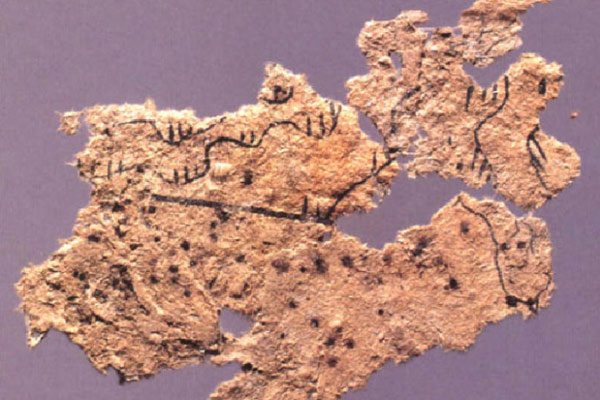
The ancient scrap of paper was unearthed 30 years ago in Gansu province. [Photo provided to China Daily] |
A Chinese archaeologist has announced new findings about an ancient scrap of paper, likely the earliest on record, dating back to 250 years before Cai Lun revolutionized papermaking technology in China.
The piece, about five centimeters long and two centimeters wide, was unearthed three decades ago in Fangmatan, an archaeological site in Gansu province, but it didn't garner attention until 2012 when Li Xiaocen, an archaeologist at Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, found the piece had uneven fiber distribution when put under the microscope.
"The surface of the fragment is yellow and quite rough, and the fibers are randomly yet densely interlaced," Li said.
"These are the traits of an ancient papermaking technology, very different from CaiLun's, that ethnic minorities in Tibet, Yunnan and Xinjiang still use to make Kongming lanterns and transcribe scriptures."
Li revealed his findings at a recent seminar, attended by more than 160 archaeologists from China, Germany, Greece and Peru.
A crude type of paper was used as early as the Western Han Dynasty (206BC-AD24). However, Cai Lun, a eunuch in the Eastern Han Dynasty (AD25-220), greatly reformed the art of papermaking and is regarded as the inventor of ancient paper and the paper-making process.
Li said the fragment predates Cai Lun's invention by about 250 years, though controversy remains over whether the fragment should be identified as real paper.
"Further research should be conducted on, for example, the degree the pulp was beaten and the entire production process as well as the paper's whiteness," according to Chen Gang, a professor with the department of cultural heritage and museology at Fudan University. "But Li's research is helpful for us to understand the full picture of ancient papermaking technology in China."