Inspections at ports to prevent risks to biosafety
China will tighten inspection and quarantine of plants and animals at its borders to prevent the entry of harmful species this year, the top authority said on Monday.
The announcement came as growing numbers of species have been intercepted at ports in recent years on the back of increasing international exchanges, posing serious threats to biosafety, according to the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine.
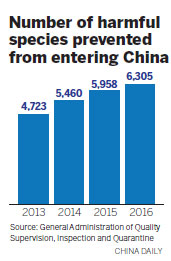
Entry-exit inspection and quarantine authorities across China intercepted 6,305 kinds of harmful species in 2016, with 26 of them being intercepted in China for the first time, Zhi Shuping, head of the administration, said at an annual conference on Monday.
The number of harmful species intercepted in 2015 was 5,958, according to administration figures.
To address risks posed to biosafety, the administration will tighten inspection and quarantine at ports, and improve monitoring of standards for animals and plants entering and exiting China, Zhi said.
Stricter measures will be implemented to improve the supervision of imported live animals, sprouts, fruits, wood and animal feed, he said.
Meanwhile, the administration will intensify inspection and quarantine of wild plants and animals to prevent the loss of Chinese species or the invasion of alien species, Zhi said.
Nearly 9,000 kinds of harmful species were intercepted between 2011 and 2015 in China, with the number of interceptions increasing by an average of 26.8 percent each year, said Zhao Zenglian, the administration's deputy director of animal and plant quarantine supervision.
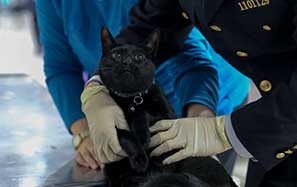
The administration has upgraded equipment and improved methods in recent years such as using computed tomography and specially trained inspection dogs at major ports nationwide.
In Beijing, officers from the Beijing Entry-Exit Inspection and Quarantine Bureau use ultraviolet rays at checkpoints to help discover prohibited items that must be stored at freezing temperatures, such as cells and biological materials sourced from plants or animals, the bureau said in December last year.
Harmful species intercepted by the bureau last year included frozen frogs, ants, snakes and various bacteria found in fruits, it said.