3-D technology helps preserve iconic heritage
 |
|
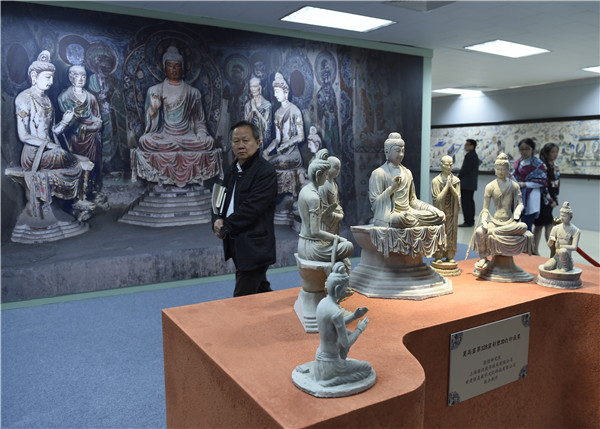
Visitors take in the Dunhuang on the Silk Road exhibition in Beijing in April. It featured 3-D printed replicas of Buddha statues from the Mogao Grottoes in Dunhuang, Gansu province.[Photo by LUO XIAOGUANG/XINHUA] |
HANGZHOU - About 2,000 kilometers from the Yungang Grottoes, a 1,500-year-old UNESCO World Heritage site in Shanxi province, a small army of 3-D printers has been working around the clock to save a cultural heritage from oblivion.
Over the past five months, the 20 machines, housed at a workshop in Shenzhen, Guangdong province, have been cranking out full-size replicas of three of the grottoes' Buddha statues. Faithful copies will soon be displayed in the eastern coastal city of Qingdao.
The grottoes contain more than 51,000 statues. But the original works, which were carved into soft stone, will gradually disappear as erosion runs its inexorable course.
"Even today, scientists are unable to stop the aging of the grottoes using chemical or physical methods," said Li Zhirong, an associate professor of archaeology at Zhejiang University who is dedicated to cultural heritage. "Therefore, the best way to protect the grottoes is to preserve their information in a scientific, comprehensive and authentic way."
Using 3-D scanners, the institute provided all the original data needed to reproduce the cave and its carvings. For a 10-meter-tall statue, the error between the original work and the replica is less than 5 millimeters.
Such technology has been employed in other projects. For example, researchers replicated cave No 220 of the world-renowned Mogao Grottoes in Dunhuang, Gansu province. During the project, the team used newly developed equipment to record every detail of the frescoes, which date to the Tang Dynasty (618-907).
After making high-resolution images, the team used software to stitch them together into a single picture with high precision, said Diao Changyu, a computer specialist.
The technology can also help solve archaeological mysteries, researchers say. For instance, the team helped identify a badly damaged stone tablet last year after collecting 3-D images of it.
Xinhua