Best Chinese Universities Rankings
|
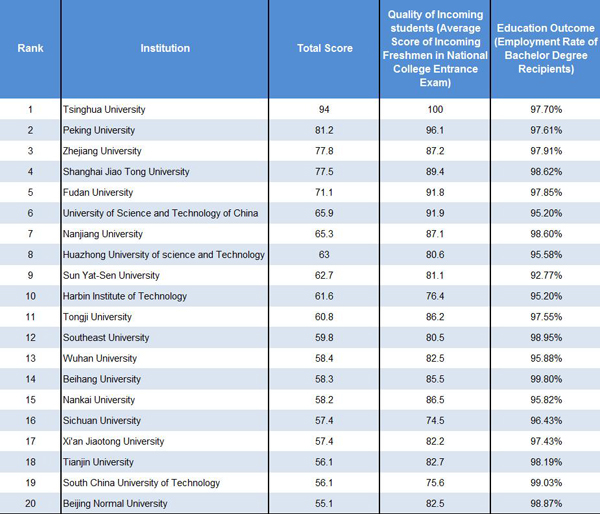 |
| Top 20 of Best Chinese Universities Ranking • Overall Ranking 2017 |
Best Chinese Universities Rankings (BCUR) is released by ShanghaiRanking Consultancy every year. It uses indicators that can represent underlying judgments of universities by different types of stakeholders such as students, employers, academics and industries. BCUR employs nine key indicators to rank Chinese universities, making the rankingsmore relevant, reliable and easier to understand. What’s more, BCUR is committed to be a fully transparent service as it publishes not only the detailed methodology and data sources but also raw data of all evaluated indicators, which enables users to verify the results or do further analysis.
Methodology
Which universities are considered for the ranking?
BCUR considers all 1216 universities in the list of universities and colleges that can grant bachelor’s degrees recognized by the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China (published May 21, 2015), which consist of 793 public universities,140 private universities and 283 independent colleges.
The universities ranked in BCUR 2017 include:
1) Universities with a minimum undergraduate enrollment of 100 (2015).
2) Universities with a minimum publication of 100 papers indexed by Scopus (2011-2015).
Ranking Criteria and Weights
BCUR ranks universities according to their performance in four dimensions: teaching and learning, research, social service and internationalization.
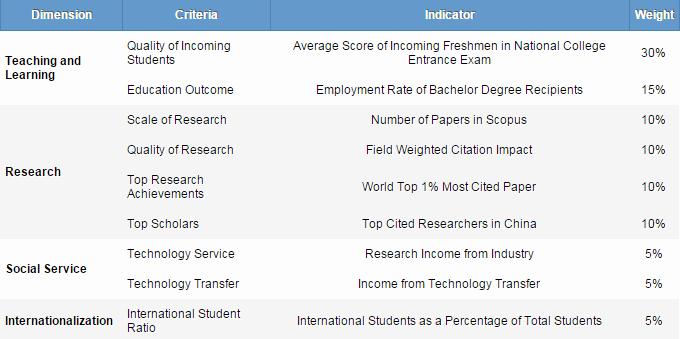
For each indicator, the highest scoring institution is assigned a score of 100, and other institutions are calculated as a percentage of the top score. Scores for each indicator are weighted as shown above to reach a final overall score for an institution.
Definition of Indicators
Quality of Incoming Students
The indicator to measure Quality of Incoming Students is the average score of incoming freshmen in the national college entrance exam, which reflects the recognition of parents and students of universities’ reputations for excellence in teaching and learning.
Source: http://gaokao.chsi.com.cn/, a government-authorized website.
Education Outcome
The indicator to measure Education outcome is the employment rate of bachelor degree recipients, which is a direct reflection of employers’ acceptance of universities’ graduates.
Source: 2015 Chinese College Graduates’ Employment Quality Report, Teaching Quality Report of the Undergraduate released by each university or other authoritative sources such as a provincial education authority.
Scale of Research
The indicator to measure Scale of Research is number of papers (articles and reviews) indexed in Scopus from 2011- 2015. Publication is an important outcome of scientific research; thus the number of papers published can reflect the scale of research activities in universities.
Source: Scopus database.
Quality of Research
Quality of Research is measured by Field Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI). Citation has been widely used to evaluate the impact or quality of scientific papers in research evaluation. However, since significant differences exist among citations in different fields, years or types of papers, it could not be used for interdisciplinary comparison without being normalized. FWCI is a normalized indicator recognized internationally as the best quantitative indicator for measuring the quality of scientific papers. FWCI calculates the ratio of citation of papers (articles and reviews) published by each university during the period of 2011-2015 to the average citation of papers in the same field, of the same year and same type.
Source: Scopus database.
Top Research Achievements
Universities’ Top Research Achievements is measured by the number of papers among the top 1% of papers most cited in the world in each field during the period of 2011-2015, which reflects the academic influences of each university.
Source: Scopus database.
Top Scholars
The indicator of Top Scholars is the number of most cited researchers in each field in China. The total number of most cited researchers is around 1770, and the field distribution of those researchers is based on the distribution of total Chinese researchers in each field. The standards for selecting the most cited researchers are objective and unified, and are based on researchers’ academic influences.
Source: Scopus database.
Technology Services
Research income from industry is used for measuring Technology Service. One of the main approaches for universities to serve economic development is to solve scientific and technical problems in industries using their knowledge and talent base; therefore the competence of universities in technology services is reflected by their income from industry.
Source: Science and Technology Division, Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China. Compilation of Statistics on Science and Technology of Higher Education in 2015. Beijing: Higher Education Press.
Technology Transfer
The income from technology transfer is a proxy for the contribution of a university’s research output to economic development.
Source: Science and Technology Division, Ministry of Education of People’s Republic of China. Compilation of Statistics on Science and Technology of Higher Education in 2015. Beijing: Higher Education Press.
Internationalization
The indicator to measure Internationalization is the international student ratio, where student includes undergraduates, master students and doctoral students. The ratio reflects the international reputation of the university as well as the university’s ability to provide students with an international education environment.
Source: (1) ShanghaiRanking’s Data Exchange Program (DEP). (2) Official statistical reports published by the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China.


















