Secrets of Women's Underwear
Updated: 2007-05-29 11:33
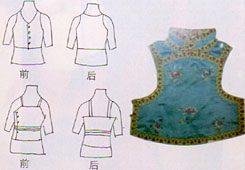
"Liangdang"
"Liangdang" appeared in the Wei and Jin dynasties. It is believed that it was introduced into the central plains by nomads from northern China.
On the mural painting unearthed from a tomb from the Wei and Jin period in the Gansu Province, there were fragments of women wearing square-shaped "liangdang." A brocade of rich colors was the major material for the double-pieced underwear, which could protect both chest and back.
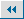
"Hezi" in Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty saw economic prosperity and also a quite open society, which influenced the changes of the undergarments. It was in this period that the first lace-less underwear appeared. It was called "Hezi." The women during this time preferred to wear translucent dresses which exposed the neck, shoulders and upper-half of the breasts - making laces redundant. Instead, buttons were fastened in the front to fasten the "Hezi," a piece of cloth that swathed the breasts and back. It was made from a heavy, elastic fabric, making a better visual effect for the breasts.
"Moxiong" in the Song Dynasty was much more conservative. The single-pieced underwear could cover both the breasts and belly. In the common families, "moxiong" was usually made of cotton; rich women could afford silk ones that were embroidered with a flower design. One double-layered "moxiong," made of thin silk, was excavated at a tomb in the Fujian Province.
During the Yuan Dynasty, underwear became much more tempting, whether seen from the name or from the shape. "Hehuanjin," the name in Chinese alludes to the close relationship concerning sex. Several bands, which were connected to the front piece, served as the only covering on the back. This exposed a lot of skin. Buttons were fastened in the front, similar to the "Hezi." It was usually made of thick brocade.
In the Ming Dynasty, the colors of women's clothes were restricted to purple, purplish green, peach and other shallow colors. Red, yellow and black were strictly forbidden. The underwear "Zhuyao" resembled a jacket, with laces near the waist, which could be adjusted to show off the female's curves.
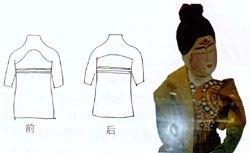
Qing Dynasty saw the bloom of the well-known "Dudou," or bellyband. Usually, a bellyband is made into a diamond shape. Lace is placed near the neck and the waist to be fastened and to accentuate the curves of the torso. The lower part of a bellyband is an inverse triangle to cover the belly. Designs of tigers, scorpions, snakes and geckos were embroidered to ward off evil spirits. Themes of love, such as lotus and pairs of mandarin ducks, were also common on bellybands. Silk and cotton were the most used materials. Sometimes gold chains were also used by women from affluent families, while silver and copper chains were adopted by the middle-class.
Because of the Republic of China's openness to the outside world, "Majia," something similar to the western corset, became popular among women.