Symbols, superstition and playing the numbers game
 |
|
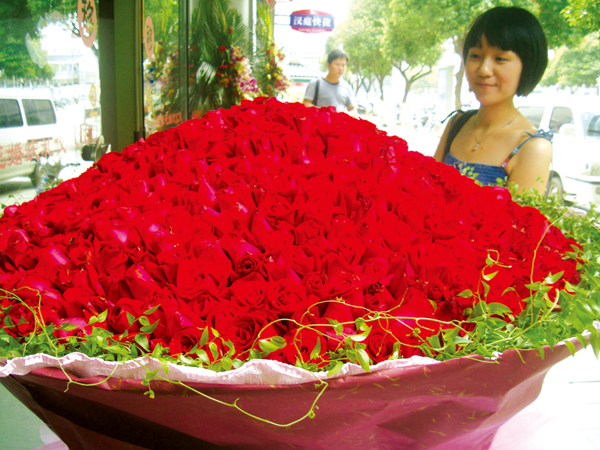
A bouquet of 999 roses displayed at a flower shop attracts a passerby's attention. Wang Jiankang/For China Daily |
At the other end of the spectrum is the number four, a homonym for "death". Some Chinese refuse to purchase a cell phone number with the digit, calling it "taboo". Also, many buildings in Hong Kong and the mainland do not designate a fourth floor so that the fifth floor immediately follows the third, as shown on elevator buttons.
Why is Chinese culture so infused with what seems to be numerical superstition? And what has kept these beliefs strong in modern times?
"It's part of the Chinese people's culture to use symbols to represent themselves," says Lee Cheuk-Yin, head of the Department of Chinese Studies at the National University of Singapore and a specialist in Chinese history and traditional culture. "They like to use symbols, because Chinese culture is more conservative and implicit."
A principle of this symbolism, Lee says, is the use of punning a play on words based on the similar pronunciation of different characters. This also explains, he says, why the Chinese consider fish and bats auspicious animals. "Fish" is a homonym for "abundance" in Mandarin, while "bat" sounds like "good fortune".
Using this principle, the Chinese have also come up with auspicious number combinations. Some of the most popular, according to a paper by Chen Rudong, a professor at Peking University's Department of Communication Studies, are: 168 (which sounds like "to always be rich"), 518 ("I shall be rich") and 666 ("everything will remain well").
These beliefs end up being passed on for generations since people develop an emotional attachment to symbols.
"Encountering a symbol, whether it's a number or a word or a picture, is a bit like encountering the thing itself, leading to a bit of ambiguity in the brain," says Matthew Hutson, author of The 7 Laws of Magical Thinking: How Irrational Beliefs Keep Us Happy, Healthy and Sane.