Jilin builds TanSat's carbon dioxide detector
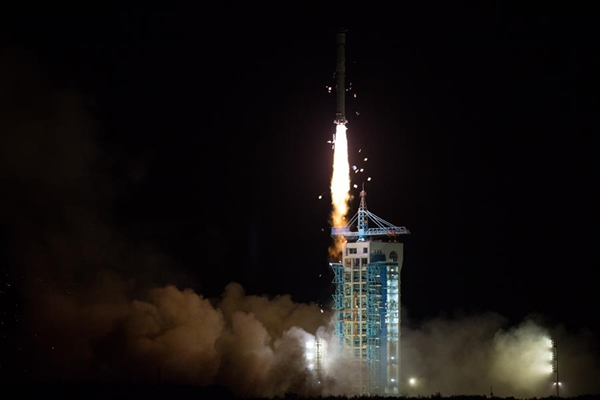
TanSat, China's first carbon dioxide monitoring science satellite, carrying two main greenhouse gas detecting instruments, both developed in Changchun, Jilin province, to monitor and understand global carbon dioxide distribution and to help restrain greenhouse gas emissions, was successfully launched on Dec 22.
 |
|
TanSat, China's first carbon dioxide monitoring science satellite, successfully launches from the Jiuquan Space Launch Center on Dec.22. [Photo/Xinhua] |
The two main payloads on Tansat — a high-resolution Carbon Dioxide Spectrometer and a Cloud and Aerosol Polarimetry Imager (CAPI) — were entirely developed by the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics, and Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The research program was initiated in 2011 and required six years of development by the young team, with an average age of under 35, to conquer difficulties in designing payloads, developing technologies, and manufacturing the final instruments.
 |
|
The research team poses with the payload which is to be carried on TanSat and wish for a successful launch. [Photo/chinajilin.com.cn] |




 Mail
Mail Print
Print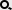 Larger
Larger
