Standardization is closely related to everyone's life. Standards have played an extremely important role in the fields from the daily basic needs such as clothing, food, housing, and transportation, to enterprise's industrial technology and research, and to the country's major construction projects at every crucial moment. It is because of its pervasion in all aspects of life that people have not paid attention to its creation, application and protection. In fact, it can be seen every day that there is a group of people who is busy working for it, and a strict regime and system to govern the creation, implementation, and protection of it. Due to those unnoticed systematic mechanisms. There can be a guarantee for the satisfaction of the common's needs and the maintenance of social stability.
What Is the Meaning of Standard?
Sun Xiaokang, Deputy Director of the Standardization Administration of the China (SAC) pointed out: "What is meant by standardization is a set of regulatory documents, which is used by all and repeatedly through consensus and being approved by an authority, to achieve maximum consistency. Put in popular words, maximum consistency has to be achieved in a certain industry, as, e.g., the IT products that we process, in order to meet the social needs, must satisfy maximum consistency. Such consistency must be approved by an authority, and this authority in our country is the Standardization Administration of China. Industry standards are approved by relevant authorities. The approval documents are used by all. International standards are used by many countries repeatedly over and over again. Therefore, the best result of certain industry will form into documents, to be used over and over again, hence, standardization."
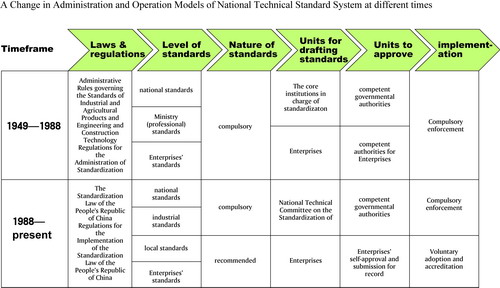
There are four systems of standardization. National standards are drafted and promulgated by the SAC; industry standards are formulated by related departments and committees under the State Council and act as a guidance for processing, manufacturing in certain industries; local standards are set up by local governments to meet the needs of local economic development; corporate standards are planned by a particular company itself in its procession and manufacture in order to regulate its production and business activities. The last kind of standards includes compulsory and exemplary standards, and the compulsory standards are the basic requirements for product quality, which must conform to the stipulations of State laws and regulations.
China's Progress in the Development of Standards in Recent Years
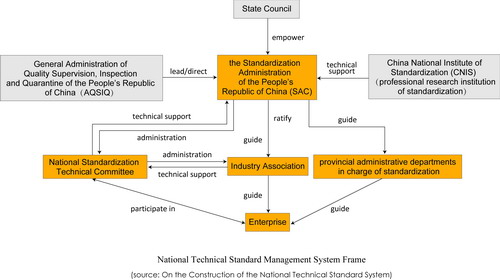
Standardizational work has been increasingly valued in China in recent years due to rapid changes in the international environment after the rapid development of international trade. Professional services have been done by SAC, China Association for Standardization, China National Institute of Standardization (CNIS), and a series of other units and groups, which have provided China's standards with important support. Take CNIS for example. It has undertaken dozens of national key scientific and technological projects and National Programs for Science and Technology Development (NPSTD) since 1990.

Among its completed projects, there are three worth special mention, which belong to the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China during the 10th Five-year Plan. These are A Study on the Development Strategy of China's Technical Standards, On the Construction of the National Technical Standard System, and Basic Studies on and Technical Measures for China's Major Food Security Standards, which have provided important intellectual support for China's standardization development. CNIS president Wang Zhongmin commented: "As far as energy-saving and environmental protection is concerned, CNIS has played an important role in the quality improvement of energy-consuming products and enhancement of energy efficiency products according to the road map of working out energy efficiency standards, promoting energy efficiency label, and implementing an energy saving standard policy beneficial to the people.
CNIS has undertaken the administration of energy efficiency labels on 21 categories of products in 6 batches, resulting a cumulative saving of more than 1,500 kilowatt hours within 5 years, a reduction of 140 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions, and made a significant contribution to the achievement of target for energy saving and consumption reduction per unit of GDP during the period of 11th Five-year Plan. Furthermore, CNIS has also actively given assistance to the research and implementation of the State's financial subsidies to energy-saving products in order to establish a long-term mechanism for the popularization of high efficiency energy-saving products on the basis of consumption of such products by way of the project of energy-saving products for the people."
Meanwhile, it has attached an increasing importance to the coordination between China and the world in the fields of standardization. After years of hard working, China has become a permanent member in the Council of the International Standards Organization, thus having a major voice in deciding important affairs in ISO. It is shown by statistics that there are 164 draft standards submitted by China and listed on the agenda of ISO and IEC, and 66 of them have been ratified and become official international standards. Professionals in standards industry deem it a very big step forward. China is making great efforts to make Chinese standards a more and more important weight at international panel.
According to Steve Mills, President of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), there are a considerable number of Chinese enterprises which have participated in the formulation of a large number of international, national and industry technical standards related to many industries since 2002. There are many examples in this regard. Jointly with other domestic enterprise, Lenovo Group successfully put forward IGRS for the intelligent interconnection among IT products, home appliances and communication equipment. TDSCDM developed by Datang Telecom Technology & Industry Group has become one of the three major 3G standards after its being recognized by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). AVS audio and video technology and system standards have also been approved as national standards for IPTV, mobile TV and other emerging industries. These standards are conducive to the maintenance of domestic market and opening of international markets for Chinese high-tech enterprises, which will fundamentally change the history that Chinese enterprises have to follow foreign standards.
Few know the arduous task behind these achievements. According to Wu Zhengping, Vice Chairman of National Technical Committee on the Standardization of High Frequency Cable and Connectors of SAC, Vice Chairman and Secretary-general of Subcommittee on Radio- Frequency Connectors of National Technical Committee on the Standardization of High Frequency Cable and Connectors at the Technical Committee, Technical Committee on Standardization, has submitted 30 draft international standards to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) since 2005, of which 10 have been released as IEC standards. However, the Chinese series of international standards for semi-flexible communication cable consisting of eight standards were almost stranded in the new project proposal stage, and passed at the key new project (NP) voting phase after arduous efforts, and has entered the final voting stage of the Commission up to present. It is expected that they will become the official IEC standards in 2011.We can be proud of these achievements on one hand, and bear in our minds that there is a long way to go for the internationalization and systemization of Chinese standards.
Enterprises' Difficulties in Gaining access to Standards
In practice, many companies are puzzled that they do not know there are standards in certain fields despite such standards have been established, that they have no access to the documents of standards and that they have no idea of how to follow these standards. In this regard, SMEs and the new emerging businesses have met with more problems than the above-mentioned.
Sun Xiaokang commented: "All texts and e-files may be obtained through normal access, such as China Standard Press, or Institute of Standardization at provincial levels where standardization texts are available. Meanwhile, information regarding National Standards may also be obtained from or be purchased by contacting government ministries. You can also get information from the websites of Standards Press of China and distribution system of standards through internet. You should frequently visit WWW.SAC.GOV. CN, the website of Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China, where you can find the latest announcement of national standards, look up national standards plans and the abolished state standards. Each unit and individual can look up the information related to the amendment of national standards and the directory of all national standards, and can read the full text of mandatory national standards online for free."
Copyright Protection for Standards: a Long Way to Go
A copyright infringement was investigated on November 26th, 2010 in Wuxi City, Jiangshu Province. Competent authorities were informed that illegal copies were released to trainees in a program for engineers of standards application titled by GB/T1.1-2009 and GB/T20000.2- 2009. China Quality Inspection Press requested Wuxi city law enforcement to deal with the case in violation of standards. 42 sets of illegal standards were confiscated. This case is a warning and should be mentioned to those seeking to promote China's standardization work. It shows that people may have neglected copyright protection of standards at times while focusing on the formulation of standards, the research of technology, and other issues.
Relevant departments have attached increasing importance to the copyright protection of standards with the development of national intellectual property strategy. On November 16th, 2010, SAC and the Certification and Accreditation Administration of the People's Republic of China (CNCA) jointly issued a Notice of Further Crackdown on the Infringement and Piracy Related to Standards in order to Strengthen the Copyright Protection of Standards (Notice), which gave more detailed information to The Notice from General Office under the State Council of Printing and Distributing the Special Action Plan for the Crackdown on IPR Infringement and Selling Counterfeit and Shoddy Goods and The Notice from National Administration of Quality Supervision on the Implementation of the Special Action Plan for the Crackdown on IPR Infringement and Selling Counterfeit and Shoddy Goods issued by the State Council. According to the Notice, the crackdown on the infringement and piracy of standards is an important component of the two crackdowns (on IPR infringement and selling counterfeit and shoddy goods), which would provide copyright protection with legal standards.
The Notice pointed out that there are many kinds of infringement, including dissemination or selling of standards after converting full-text of standards into database(s) without authorization; using of pirated standards in accreditation, consultation, training, public administration and public affairs; reproduction of standards in large quantity and dumping it at lower price, and so on. There are many errors in these pirated standards, including a higher ratio of missing and mistake between the lines, out-of-date standards purported to be effective at present, and distorting and forging data.
All these defections do harm to the authority, accuracy, and seriousness of standards to a considerable extent. In accordance with national regulations, standards at national, industrial and local level shall be published by press designated by the departments which are empowered to approve and issue standards concerned. According to the provisions of relevant international agreements, the right to copy and sell the publications of ISO/IEC standards publication shall be entrusted to designated units pursuant to SAC's authorization. Legitimate copies of standards shall be used in production and business activities of enterprises and institutions, in the process of inspection, verification, accreditation, consultation and training activities for standardized service institutions and intermediaries, and in the administrative supervision and inspection, law enforcement and investigations, administrative licensing and other official activities by governmental agencies.
The Notice stipulates six kinds of copyright infringement actions done by any unit or individual against the copyright of standards: (1). reproduction of any part of standards (without consideration of the versions of standards, including paper, online, electronic, CDROM) without permission of departments in charge of standards approval and issuance; (2). distribution of any part of standards by way of electronic information network or developing databases from standards without permission of departments in charge of standards approval and issuance; (3). printing and distributing standards and their compilation without permission of departments in charge of standards approval and issuance; (4). printing, distributing, and disseminating standards and their compilation in the name of "internal data" without permission of departments in charge of standards approval and issuance and the license for printing internal data; (5). printing and distributing unapproved or unreleased standards without permission of departments in charge of standards approval and issuance; (6). reproduction, sell, dissemination, translation and publishing of all publications and relevant documents of ISO / IEC standards without SAC's empowerment.
Supporting System: Need to Be Optimized
As far as the supporting system for the copyright protection is concerned, Sun Xiaokang made comments as follows:
"At present, relevant departments are working to create a good environmental for standards researches. For example, timely trainings have been placed on the agenda for experts and members from standards formulating organizations such as the Technical Committee and its subcommittees, working groups, project team members and other organizations, in order to improve their professional level and the quality of standards in the end. Then, there should be a social oversight on the enforcement of standards after its being worked out. Therefore, we should strengthen the cultivation and training of talents specialized in standards for enterprises. At last, more social attention should be paid to standardization to win support from public opinion and mass media, which is indispensable to enhance the standardization in China."
"Meanwhile, SAC is developing the national platform for standardized resources and information, which is of great concern to business and the masses. Enterprises need standards to do business, and foreign standards for international trade. Consumers want to know the matching degree of purchased products with national standards. The State has given financial support to the development of the national platform for standardized resources and information. When the platform goes into operation, we may look up all kinds of standards, whether they are national, international, foreign, industrial or local. What's more, we can find some recommended standards and have a look at its directory and contents."
(Translated by Yuan Renhui)



