Taking the heat off the solar dispute
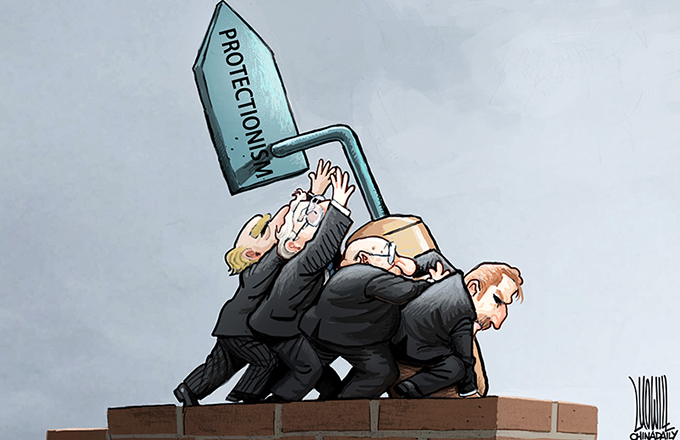
The global solar photovoltaic (PV) products' sector faces a new challenge in the form of trade disputes between major producers and consumers. These disputes are quite testing, because there is a fine balance between creating a level playing field in the market and the need to make solar technology more affordable for the majority of the global population.
Following the recent imposition of 11.8 percent interim anti-dumping duty by the European Union on solar PV products imported from China, including panels, cells and wafers, the issue has become highly politicized between the two sides, among the EU member states and the key players of the solar PV industry.
Subsequently, the EU and China have held negotiations on "price undertakings", with the EU saying Chinese solar panels would be sold at a certain minimum price in the European market. These trade talks were initiated at the annual EU-China ministerial-level meeting of the joint economic and trade commission in Beijing on June 21. China's Minister of Commerce Gao Hucheng and EU Trade Commissioner Karel De Gucht co-chaired the talks, where trade issues, including the solar panel dispute, were discussed.
The negotiations are continuing and, under the current proposal, the total power-generating capacity of Chinese PV modules imported by EU should be below 10 gigawatt a year, with a minimum price of 0.5 euro per watt. This will make the prices of Chinese solar products sold in the EU more comparable to those of European panels.
Both sides, however, are under pressure to reach an agreement before Aug 6, failing which the EU will raise the anti-dumping duty to 47.6 percent, which could be followed by an EU decision in December to continue with the anti-dumping duty for the next five years.
There are several reasons why the EU and China should reach an agreement on the issue which allows both sides to save face and will facilitate the healthy development of the global solar products' industry.
First, such an agreement is necessary to prevent the EU-China trade conflict from spilling beyond the solar PV panel sector. Beijing has already initiated an investigation into EU wine exports to China. To prevent the row from escalating into a full-scale trade war and harming long-term EU-China cooperation in fields such as clean energy and climate change, the two sides have no option but to find a workable solution.
Second, an agreement on solar panels will help the EU and China, as key players in climate change negotiations, maintain a good working relation and reach a fair, ambitious and legally binding climate agreement under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change in 2015. If the solar panel issue is not resolved amicably, it will cast a shadow over EU-China relations and could further delay a binding climate agreement at the already protracted climate talks.