Green energy a real solution to climate change
 |
| LIU XINYI/CHINA DAILY |
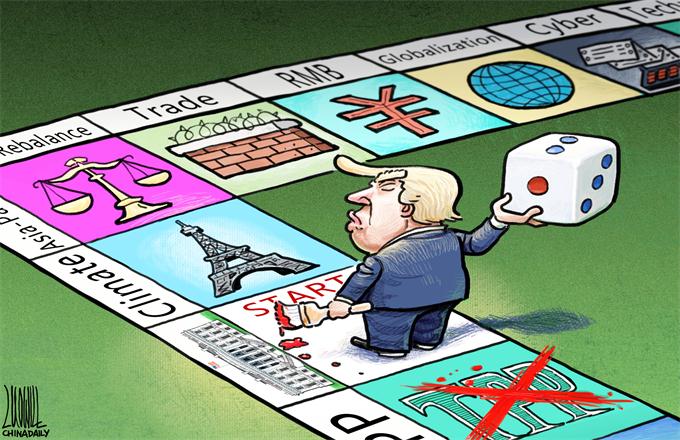
Thanks to the election of Donald Trump as the next United States president, diplomats and governments around the world are wondering what to expect from the next four years. When it comes to climate change, many environmental campaigners are alarmed, which is understandable because Trump has sent mixed signals and the world does not know anything about the incoming US administration's plans in other areas.
But there could be cause for hope, and even a potential opportunity for China.
Climate change is real and mostly man-made. On the presidential campaign, Trump said he would dump the Paris Climate Treaty. And although after the election he said, "I have an open mind to it", it appears unlikely the US will fulfill the carbon cutting promises that were made by the Barack Obama administration.
But instead of being a world-ending event, it offers an opportunity for other countries including China to step forward and lead the way with a smarter approach.
Even if it were to survive, the Paris Treaty by itself would do very little to reduce the effects of climate change. The United Nations estimates that if every country were to make every single promised carbon cut between 2016 and 2030 to the fullest extent, carbon dioxide emissions would still only be cut by one-hundredth of what is needed to keep temperature rises below 2 Celsius.
The problem is that these feeble promises will be costly. Today's green technology is inefficient and requires significant subsidies. Trying to cut CO2 emissions, even with efficient taxation, makes cheap energy more expensive, which would slow economic growth.
Calculations using the best peer-reviewed economic models show the global cost of the Paris promises-through slower GDP growth from higher energy costs-would reach $1 trillion to $2 trillion every year from 2030.
China has promised to cut its CO2 intensity by 60-65 percent by 2030. Studies suggest that a 60 percent cut could cost about $200 billion annually in lost GDP growth. And living up to the Paris Treaty promise of peaking CO2 emissions around 2030 could cost China $400 billion or more in lost GDP. So countries, including China, should focus on finding smarter solutions.
Climate economists have found that green energy research and development are a much more efficient approach. And a panel of Nobel laureates for Copenhagen Consensus say we shouldn't just double R&D but increase it six-fold, to reach at least $100 billion a year.
Investment in ingenuity by China and other countries could help reduce the price of green energy below fossil fuels. Only then will we truly be able to reduce climate change.
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development says that about one-quarter of all development aid today comprises climate aid. But there are much more important issues the world's poorest are concerned about-2 billion people suffer from malnourishment, 700 million live in extreme poverty and 2.4 billion don't have access to clean drinking water and sanitation. The UN asked nearly 10 million people across the world for their top policy priorities. Education, health and nutrition topped the list. Climate change was at the bottom.
In general, most of the world's most pressing problems can be tackled faster and more cheaply by moving away from climate aid to providing funds for eliminating poverty and illiteracy.
Cost-benefit analysis shows that freer trade is the single most powerful way to help the world's poorest people. Reviving the moribund Doha Development Round of global free-trade talks would reduce the number of people in poverty by an astonishing 145 million in 15 years, according to research commissioned by the Copenhagen Consensus Center. Sadly, Trump's rhetoric has been consistently opposed to trade.
Commentators in the US and elsewhere remain uncertain what to expect from the incoming Trump administration. But on climate change, at least, there could be an opportunity for decisive action: going beyond dumping the ineffective Paris Treaty, to policies that will harness green energy innovation to focus on a real solution to climate change. If China embraces a technology-led policy, it has the potential to be part of the real solution to this challenge.
The author is president of the Copenhagen Consensus Center.