Inada resignation adds to Abe's woes
 |
|
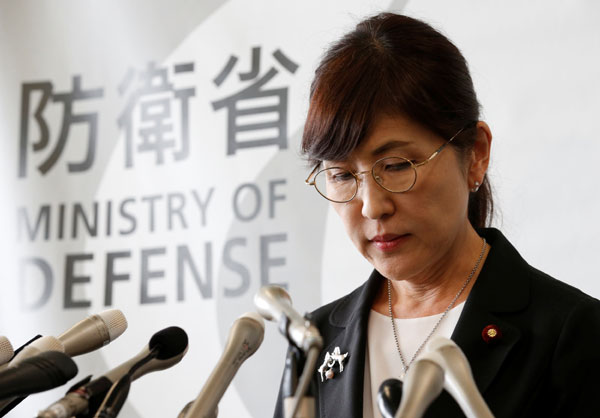
Japan's Defence Minister Tomomi Inada announces her resignation during a news conference at the Defence Ministry in Tokyo, Japan July 28, 2017. [Photo/Agencies] |
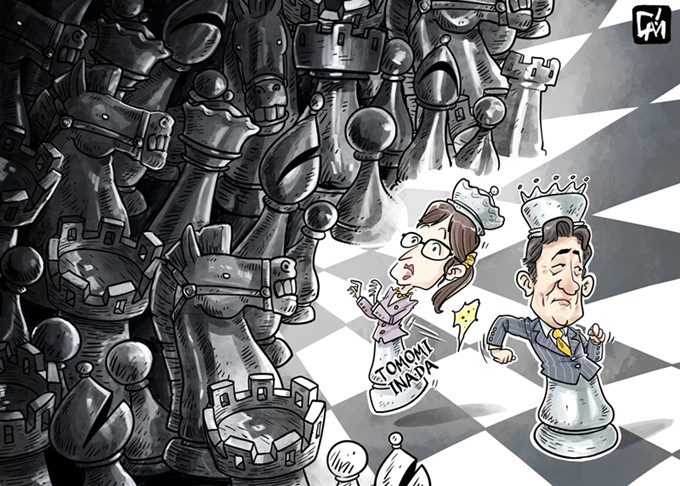
Japanese Defense Minister Tomomi Inada resigned on Friday following weeks of scandal that included the alleged withholding of internal documents, especially those on the daily activities and safety conditions of Japan's Ground Self-Defense Force during its UN peacekeeping operations in South Sudan.
Once Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe's protégé and a shining female member of the Japanese Cabinet, Inada resigned days before completing one year in office. Foreign Minister Fumio Kishida will now hold the additional charge of the defense portfolio until a new defense minister is appointed.
Ostensibly, Inada's involvement in the "cover-up" of the self-defense force's activities a year ago in South Sudan, where the Japanese troops were barred from taking part in peacekeeping operations unless the warring parties declared a ceasefire, ended her career. However, the daily activity logs of Japan's Ground Self-Defense Force suggest combat between government and rebel forces in South Sudan in July 2016.
If confirmed, the documents could put a big question mark on the legitimacy of Japan's overseas peacekeeping operations. The Japanese Defense Ministry had said late last year that the data had been deleted, but it released part of the information which was found on a computer in February.
Inada's recent missteps occurred in the lead-up to the Tokyo metropolitan election that were held on July 2. She came under fire for rallying support for the ruling Liberal Democratic Party, a move seen as the politicization of the Ground Self-Defense Force and a violation of Japan's Self-Defense Forces Act. Not surprisingly, her gaffe dealt a blow to the LDP, which won only 23 seats in the 127-member chamber, an all-time low.
Although not unanticipated, Inada's resignation could add to the political woes of Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe amid a string of political scandals and plummeting support rate, which has fallen below 30 percent in some polls, the lowest since he returned to power in 2012. Since the end of the Cold War, his predecessors with less than 30 percent popular support have all ended up stepping down within a year.
Abe's personal rapport with Inada, an outspoken political hawk, could no longer save her because his own career is in trouble. Alleged favoritism linked to a friend's business and flawed disclaimers in the face of solid evidence have undermined public trust in him and his administration.
So Abe has to make efforts to prevent his approval rating, which is still above the "deadly" single-digit level, from dipping further if he wants to seek a third three-year term next year and remain Japan's leader until 2021. And the planned reshuffle of the Cabinet and LDP leadership this week is very important for Abe to regain public support.
Of all the changes, the posts for Foreign Minister Fumio Kishida, and LDP heavyweight and former defense minister Shigeru Ishibaalso the front-runners for the LDP leadership-will be closely watched. Ishiba, who left the Cabinet to work out a strategy to replace Abe when the latter's term as LDP president expires in 2018, remains an unknown element. But no matter who gets ahead in the LDP leadership race, there is a risk that Abe will be forced to step aside by his party rivals if his support rate drops to a level that threatens the LDP's legitimacy to rule.
The author is an associate researcher at the Japan Studies Center of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences.