Ineffective sanctions highlight need for talks
 |
|
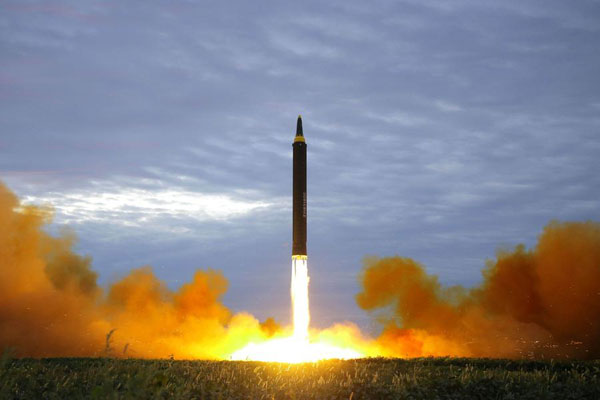
Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) Hwasong-14 is pictured during its second test-fire in this undated picture provided by KCNA in Pyongyang on July 29, 2017. KCNA via Agencies |
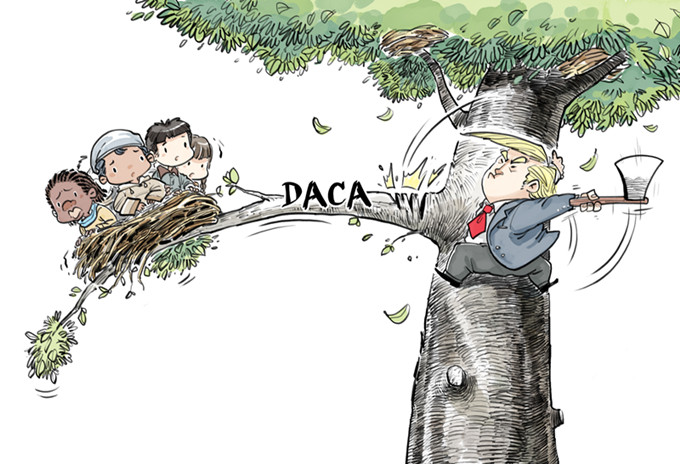
With the dust the nuclear test raised and the verbal volleys of reactions it invited yet to settle down, come reports of Pyongyang preparing to launch another intercontinental ballistic missile, which, needless to say, would further raise the hackles of the United States and Japan, and make Northeast Asia's security yet more uncertain.
What the US thinks about the DPRK found expression in its ambassador to the United Nations Nikki Haley's remarks. The DPRK leader "was begging for war", she said on Monday while urging the UN Security Council to impose the strongest sanctions possible on Pyongyang to stop its nuclear program.
The same day, US President Donald Trump told ROK President Moon Jae-in on the telephone that he would support "in principle" Seoul fitting its missiles with heavier warheads as deterrence against Pyongyang, while the ROK said it would clear the installation of four more batteries of the Thermal High Altitude Area Defense anti-missile.
Such threats of war are the last thing China wants, not least because a war would end its decades of efforts to restore peace on the Korean Peninsula in devastation, which would serve no parties' interest.
Unfortunately, the other stakeholders seem to feel otherwise, as neither the US nor the DPRK is ready to budge from its position. If this vicious circle of US threats and DPRK provocations continues, the situation one day is bound to reach a tipping point. And if either side exhausts its patience and uses even a conventional weapon, the consequences of what would follow would be catastrophic.
It may already be late but not too late to give negotiations, sincere and serious, another chance. All the stakeholders, except perhaps the DPRK, want to denuclearize the peninsula. And perhaps none, certainly not China, wants a war. Why can't then all the stakeholders use these two factors as key to begin, at least, informal talks?
The US is worried that the DPRK is inching closer to possessing nuclear weapons. But the DPRK has reached that point to counter the perceived threats, including those from the US, to its security. If Pyongyang gets a sincere assurance that its security is no longer threatened, it might, as in the past, see some reason for taking part in talks.
Sanctions have not deterred Pyongyang from its quest, nor have military threats. China has been right about their ineffectiveness, and is almost certainly right about the effectiveness of negotiations.