ROK firms' pullout reflects loss of edge
Dialogue can help resolve knotty issue

Chung Youngjune, a research fellow at the Charhar Institute and an adjunct research fellow at the Institute of Sinology at Yonsei University
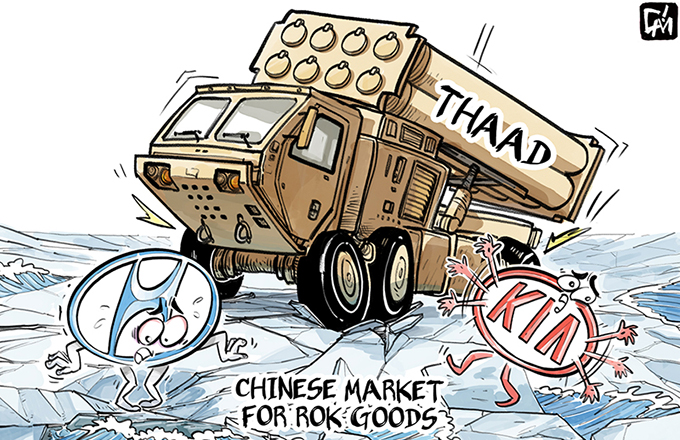
The ROK companies operating in China are exiting the Chinese market amid increasing anti-ROK sentiments and inter-governmental pressure emanating from Seoul's decision to deploy THAAD. According to rough estimates, the ROK could lose more than 1 trillion yuan ($155 billion) if its companies pull out of the Chinese market, and suffer a 0.59 percent fall in GDP. In the long term, the ROK companies will have to diversify their export markets and start reorganizing their industrial structure to better cope with external uncertainties.
Since normalization of bilateral ties in 1992, China-ROK trade has flourished, rising more than 33-fold from $6.4 billion to $211.4 billion last year. China is currently the ROK's biggest trading partner and export destination, accounting for 26 percent of all ROK exports in 2015. And the ROK, also a huge beneficiary of Chinese tourists and buyers of its cultural products, is now China's third-largest trading partner country. Therefore, the economic interdependence between the two countries will likely result in reciprocal loss of economic gains, at a time when economic vibrancy is much needed in both countries.
Seoul's decision to deploy THAAD may not prevent Pyongyang from developing nuclear weapons and missiles in the near future. China can play a crucial role as both a balancer and mediator of the nuclear talks (involving both the DPRK's nuclear disarmament and THAAD).
If the DPRK doesn't change its nuclear policy, and if the US refuses to accept Kim Jong-un as DPRK leader, who in turn refuses to accept ROK President Moon Jae-in's recent peace talks offer, then the ball might fall in the court of China and the ROK. Hopefully, the two countries can start the resolution process by holding strategic dialogues.