Chasing the dragons
Updated: 2013-10-08 07:32
By Li Yang (China Daily)
|
||||||||
My China Dream | Liew Anh Luk
He is a farmer who has tilled the soil in several countries from his native Malaysia to Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and now, China. The humble man of the land talks to Li Yang in Qinzhou, Guangxi Zhuang autonomous region.
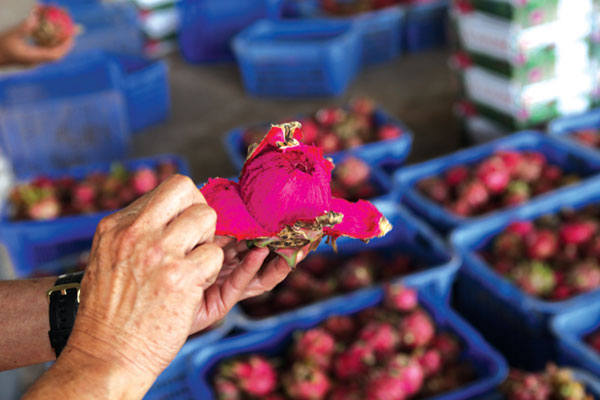
Liew Anh Luk says he sees more plants than people. After four decades working as a farmer all over Southeast Asia, Liew is continuing his pursuit of a personal vision - to plant pitaya in China.
Pitaya is a popular fruit that is more recognized by its other name, dragon fruit.
|
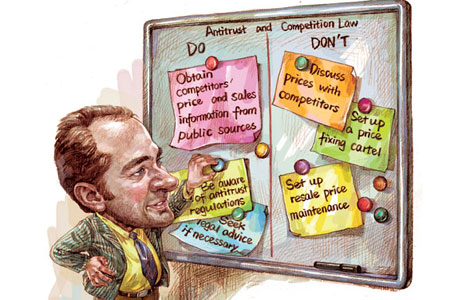
Liew Anh Luk believes that industrialization should not be an excuse for developing countries to ignore agriculture. Photos by Huo Yan / China Daily |
|
Liew not only cultivates pitaya but also hopes to make it into vinegar, wine and cosmetics. |
In China, there is a small geographical strip of land that is best suited for its cultivation and Liew came to China in 2002 to farm in Qinzhou, which is in that particular location, no more than 27,000 hectares, south of the Tropic of Cancer.
Qinzhou is the most suitable, with the right temperature and humidity, and protected from the area's frequent typhoons by the Shiwandashan Mountain ranges in the north and Beibu Gulf in the south.
"Liew is by no means an ordinary farmer and we learn a lot from him", says Zhu Yang, the special correspondent of Qinzhou city's agricultural bureau.
In response, Liew declares that he is not an expert on pitaya cultivation but that "people's knowledge on pitaya is limited".
The 63-year-old farmer is modestly garbed in worn sweaters and muddy sneakers as he paces through his farm, overgrown with wild grasses.
"This is a good way to protect the top soil. I do not want to return a patch of dead soil to the landowners 30 years later."
Liew's conscience is his guiding light.
Three years ago, he removed the organic label from all his fruits when a mill and brickyard were built next to his farm, even though his produce more than met Chinese standards.
"I simply cannot persuade my conscience not to do so."
In his opinion, only a very small part of his farm, right at the center, can still be called organic and free from contaminants.
Pitaya or dragon fruit cultivation is still considered a fledgling process and there is not much official emphasis on research and development.
"We spend a lot of time and money ourselves on research into the processes of pitaya," says Liew, who is already exploring making the fruit into vinegar, wine, juices and cosmetics.
There is already 50 million yuan ($8.18 million) invested in the business and Liew says his biggest achievement was "attracting more than 10 Chinese businessmen" to join the venture.
Lin Xingbiao, one of the largest investors in Liew's farm, says the farmer's perseverance and creativity touched him. Liao Jiyan, another investor, echoes that sentiment.
There were basic hurdles to overcome. After the rounds of land reform from the 1950s onwards, the question of who owns the land is a major problem and it took Liew a long time to sort out how to rent 270 hectares of land from about 500 families.
Most of the farmers stayed to work for him in the farms and factories, which process 50,000 tons of pitaya a year.
Liew's connection with agriculture dates back to childhood. His father died when he was seven, leaving his mother, a rubber tapper, to bring up two sons and a daughter.
He became a farmer in the 1970s after graduating from middle school in Ipoh, a city in northern Peninsula Malaysia. To support his siblings through school, Liew worked among rubber trees, oil palms and coconut palms. He later left to study agriculture management in Alberta, Canada.
In 2000, he took his master's degree at age 50.
"Agriculture is indispensable for developing countries. Industrialization should not be an excuse for developing countries to ignore agriculture," he says, sharing his insights on life.
Chinese farmers have done a great job in raising more than one fifth of the world population with only 5 percent of the world's cultivated land.
"That's why their life is not easy. But there are some other new concerns today in China," he points out. "Big international agricultural and food companies have controlled China's soybean industries by monopolizing most of the edible oil-pressing mills since the 1990s."
Liew says this lesson must be learnt and avoided in other fields, such as corn and rice.
"China should try to make breakthroughs in agricultural technology and management to win back its competence in the area", he notes. "It is hard to carry out mechanized farming in small patches of land owned by different families. The government can encourage farmers to pool resources to promote mechanized agriculture, with small machines to improve efficiency."
He says the "red line" of 12 million hectares of farmland must be guarded and soil quality must be maintained in the era of rapid urbanization.
Letting the land lie fallow is the best way to improve soil and plant quality, instead of the universal practice of applying chemical fertilizers and pesticides, he says.

"Chinese farmers use too much pesticide. They drown, instead of poison, the insects."
The answer is for food safety supervisors to take their jobs seriously to prevent the farmers from doing so and indirectly avoid the food safety crisis.
Liew believes that local governments at county and town level have the responsibility to help farmers follow market changes and help farmers choose what to plant for the best returns, and to help farmers' cooperatives connect with supermarkets directly to reduce the costs of middlemen.
"However successfully China has developed in economy and industry, it must ensure the sustainable development of its agricultural sector and protect the farmers' interests.
"Agriculture and farmers form the foundation of the nation."
Contact the writer at liyang@chinadaily.com.cn.
Huo Yan contributed to the story.
(China Daily 10/08/2013 page18)

 Victoria Beckham S/S 2014 presented during NYFW
Victoria Beckham S/S 2014 presented during NYFW
 'Despicable' minions upset Depp's 'Lone Ranger' at box office
'Despicable' minions upset Depp's 'Lone Ranger' at box office
 'Taken 2' grabs movie box office crown
'Taken 2' grabs movie box office crown
 Rihanna's 'Diamonds' tops UK pop chart
Rihanna's 'Diamonds' tops UK pop chart
 Fans get look at vintage Rolling Stones
Fans get look at vintage Rolling Stones
 Celebrities attend Power of Women event
Celebrities attend Power of Women event
 Ang Lee breaks 'every rule' to make unlikely new Life of Pi film
Ang Lee breaks 'every rule' to make unlikely new Life of Pi film
 Rihanna almost thrown out of nightclub
Rihanna almost thrown out of nightclub
Most Viewed
Editor's Picks

|

|

|

|

|

|
Today's Top News
Japan, US start joint military drill
WB cuts growth forecast for China, East Asia
Kerry hails weapons destruction
Robust home sales during holiday
China calls on the United States to stay solvent
Beijing targets polluting cars
APEC 'should take lead' in FTA talks
US, Japan warned over sea issues
US Weekly

|

|