Entering a challenging 2017 with decent momentum
While both global trade and China’s economy enter 2017 with decent growth momentum, we expect GDP growth to ease to 6.3 percent this year due to a harsher climate for China’s exports in the US, slower real estate investment and, importantly, a change in tone of policymakers towards somewhat less emphasis on growth.
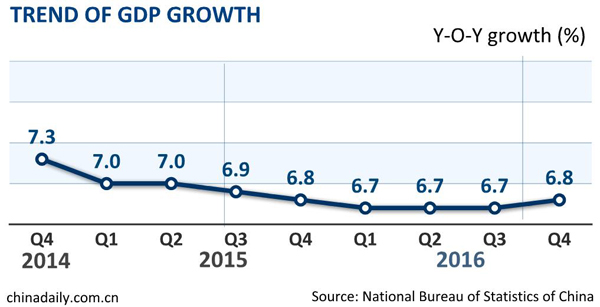
Real GDP growth edged up to 6.8 percent year on year in 2016 Q4 as services output momentum picked up. This brought whole-year GDP growth to 6.7 percent, down from 6.9% in 2015 but comfortably exceeding the “bottom line” of the 6.5-7 percent target range.
However, this was at the cost of a further rise in leverage. Overall credit – TSF excluding equity financing, including local government bond issuance – grew 16.1 percent in 2016 and overall debt reached around 2650 percent of GDP in end-2016.
Rebalancing continued last year. With the services sector outpacing industry and price changes also in favor of services, its share in GDP climbed by 1.2 ppt to 51.9 percent.
Investment momentum picked up in 2016 Q4, after having weakened mid-year, with growth of fixed asset investment (FAI) rising to 7.9 percent, supported by some improvement in corporate investment. Surprisingly, real estate FAI also accelerated again in Q4 in spite of measures taken in large cities to contain housing price increases.
Consumption remained robust in end-2016, with real retail sales growth of 9.1 percent in Q4, although passenger car sales slowed in December.
Real goods export growth slowed to 1.4 percent y/y in Q4. But the 3mma seasonally adjusted monthly export volume rose a full 4 percent in December, pointing to solid export momentum going into 2017.
Consumer price inflation eased in December to 1.9 percent y/y on lower food price increases. While the PPI rose a full 5.5 percent y/y, driven by coal mining and heavy industry, we expect the spurt to run out of steam in H1 2017 and forecast CPI inflation to remain comfortably below the likely target of 3 percent in 2017, suggesting no major monetary policy implications.
Looking ahead, recent global trade indicators show a decent momentum going into 2017 and we expect it to grow by 2.7 percent this year, from 1.4 percent in 2016. Indeed, China should in principle benefit from any pick-up in growth in the US from more expansionary fiscal policy under a Trump administration. But, while we do not expect across-the board tariffs, it is clear to us that China's exports to the US will face a harsher climate under a Trump administration, which should weigh on export growth. Overall, we expect the export outlook to improve somewhat next year, helped by the 5.7 percent real trade-weighted depreciation in the year to end-December.
Domestically, infrastructure investment should remain solid, in the year of a major leadership reshuffle. And corporate investment should benefit somewhat from renewed profit growth. But the tightening of housing purchasing restrictions in many large cities will weigh on real estate investment. We expect consumption growth to ease further on moderating wage growth, but to remain relatively solid.
Meanwhile, the messages from the Central Economic Work Conference and other recent statements suggest policymakers are moving to somewhat more emphasis on reducing financial risks and less on ensuring at least 6.5 percent GDP growth. The CEWC provided a mandate for further fiscal expansion but called for a less generous monetary stance. We do not expect a benchmark interest rate rise this year but expect policymakers to guide overall credit growth down to around 14 percent in 2017.
Overall, we expect GDP growth to slow to 6.3 percent this year. High uncertainty means that Chinese economic policymakers will want to keep options open. But at least the reasonable current growth momentum gives policy some two-way leeway.
The author is the Hong Kong-based head of Asia economics for Oxford Economics