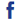Guilin's art river: charting the source of China's masterpiece
 |
|
The classic way to enjoy the scenes along the Lijiang River is to ride a tourist barge from Guilin to Yangshuo. [Photo provided to China Daily] |
The Lijiang's iconicity in art is a relatively recent invention.
From a source high in the Mao'er Mountain the Lijiang River sweeps south toward Guilin and into the world's imagination. Millions each year take to its waters, weaving between poetic peaks and submerged islands in search of scenery that arguably epitomizes Chinese landscape beauty. The Lijiang River scenery was even selected as a suitably phantasmagoric location for the Star Wars films.
In the world's eyes, Guilin's karst hills and jade waters are quintessential China. Images of Guilin's iconic karst peaks dignify conference rooms and lobbies across China and grace China's office at the United Nations and her embassy in Washington D.C. The use of the Lijiang River as an emblematic subject of Chinese landscape painting received the ultimate stamp of approval when it was pressed on the 20 yuan banknote.
Gregory Michiels, a Belgian photographer who now calls Guilin his home, says the distinctiveness of Guilin lies in "the uniqueness and the endless rhythms of the karst hills. The sea of clouds sunrise with the karst hills sticking through the clouds is magical. The scene of cormorant fishermen with the karst hills as background takes you back to ancient times."
When former US President Bill Clinton visited Guilin he observed, "Nowhere is like Guilin. It makes me think of the traditional Chinese paintings." As Clinton's remark suggests, our conceptions of Chinese landscape beauty are shaped by the ancient aesthetics of Chinese shanshui painting, that has its roots in the fifth century. Shanshui paintings have defined structural principles and typically depict landscapes using a brush and ink, rather than paints. Mountains, rivers and waterfalls are popular subjects, particularly mountains, which are sacred in Taoist culture.
Like many apparently venerable traditions, Guilin's figuration as the emblem of Chinese landscape painting is actually a recent invention. In the greatest age of Chinese shanshui art, from the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms (907-960) to the Northern Song (960-1127), its major inspiration was the gently rolling landscapes of southeast China, where Dong Yuan and Ju Ran painted soft hills and rivers with rubbed brushwork. Meanwhile a rival northern school of artists like Fan Kuan and Guo Xi used ink wash, starkblack lines and sharp dotted brush strokes to evoke rough-hewed northern mountains.
At this time Guilin was known as a remote, contested space on the wild western edges of empire. Bleeding into a politically fluid Yunnan to the west, the area was dominated by non-Han tribes, including the majority Zhuang. The first artist to paint the Guilin landscape is held to be Mi Fu (1051-1107), sometimes called the father of "Chinese impressionism". Mi Fu's used different ink shades, and large dots applied with a flat brush to render slowly flowing landscapes of rivers and clouds. His pioneering abstract style made him disliked at the Northern Song (960-1127) court. Although he was a native of Shanxi, in around 1070-1075, 20 year-old Mi Fu worked as a military senior official in Guilin. Many experts belief that Guilin's misty landscapes had a great influence on his artistic evolution.