Rerouting nerves may aid bladder control
(AP)Updated: 2006-12-19 09:55
WASHINGTON - Needing a wheelchair isn't always the biggest complaint of people left paralyzed by spinal cord injury ! it's also the loss of bladder control. On Monday, Michigan doctors began a unique experiment to see if rerouting patients' nerves just might fix that problem.
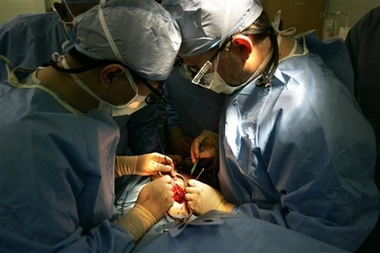 Dr. Kenneth Peters, right, of William Beaumont Hospital in Royal Oak, Mich., and Dr. Chuan-Gao Xiao of China, left, operate on Kevin Conkey on Monday, Dec. 18, 2006. [AP]  |
But if it works, merely scratching the thigh should signal the bladder to empty, allowing patients to ditch their despised catheters and restore a longed-for degree of freedom, as well as fewer bladder infections and other serious complications.
"I've got nothing to lose by doing this," is the way a cautiously hopeful Kevin Bryant, 19 and paralyzed from the waist down by a car crash, approached the experiment.
It's a technique pioneered in China that is starting to garner international attention ! and surgeons at William Beaumont Hospital in Royal Oak, Mich., hope their new US study will prove if the approach really is a solution for at least some patients.
"We're very excited," says Dr. Kenneth Peters, Beaumont's urology research chief, who headed a team of doctors that traveled to China last February to watch Dr. Chuan-Gao Xiao operate at the Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
"We said, 'This is something we need to study ... to see if we can reproduce this in the US,'" adds Peters, who in turn invited Xiao into Beaumont's operating room Monday. If the results hold up, "it would allow us to treat those patients who have no other alternatives."
Monday's first volunteer: a 49-year-old paralyzed from a car crash, Kevin Conkey of Fenton, Mich. On Thursday, Bryant, the 19-year-old paraplegic, undergoes the procedure ! in addition to a child with spina bifida, an improperly formed spinal cord that can cause similar bladder dysfunction.
After infancy, the brain takes over control of urination. The bladder sends "I'm full" signals up the spinal cord. Once the person's in an appropriate spot, the brain signals back to the bladder to empty.
In spinal cord injury and spina bifida, that control is disrupted, leaving patients either unable to urinate or constantly wet. They depend on catheters to empty the bladder every few hours. Still, recurrent infections and even lifethreatening kidney damage from backed-up bladders are common, not to mention the inconvenience and even embarrassment the procedure brings.
"People put so much emphasis on walking. I don't care if I walk again; that's not the No. 1 thing," says Bryant, of Rochester Hills, Mich. Going to the bathroom is "such a hassle in day-to-day life. I have to schedule my life around the times when I'm going to catheterize."
Xiao's procedure can't restore sensation, but uses intact nerves below the spinal injury to try to create a reflex that bypasses the brain.
"Thinking over the (urination) process, its final step is just a signal to the bladder to contract," Xiao explained in an e-mail interview. "Can we find another way to send a signal to initiate bladder contraction and voiding?"
First, surgeons remove a piece of bone alone the lower spine to expose spaghetti-like nerve roots beneath. They reconnect a lumbar nerve responsible for thigh sensation to a sacral nerve that would normally open the bladder.
It can take a year, maybe longer, for the two nerves to grow together, and people with certain bladder or spine scarring aren't candidates.
But Xiao says 110 spinal cord injury patients and 230 with spina bifida have undergone the procedure, including two at New York University where he began the research years ago. He has reported a fraction of those cases in respected urology journals, suggesting about 80 per cent resume voiding eventually.
In the Michigan study, doctors plan to suspend operating after six or eight patients, to resume only once, if, there are signs of success.
"I'm surprised that more people haven't done this before," says Dr. John McDonald, spinal cord injury chief at the Kennedy Krieger Institute and a former physician for the late Christopher Reeve.
He calls the method a logical next step from nerve-grafting for other injuries that takes advantage of primitive bladder reflexes at the spine's base. "It's very reasonable to take this approach with the bladder."
"As a field, neuroscience is revisiting the adaptive capabilities of the spinal cord below the level of the injury," agreed Dr. John Martin, a neurobiologist at Columbia University Medical Center ! but who cautioned patients to await the research. "Some of these ideas that look good haven't come to fruition."
There are some risks, Peters cautioned, including general anesthesia and wound infections. For children with spina bifida who can walk, rerouting the thigh nerve causes a small risk of some foot weakness.
And it will be expensive, about $30,000 to $40,000 a person, he estimated, a tab Beaumont is funding through a private donor.
|
||
|
||
|
|