Study seeks DNA clues on homosexuality
Updated: 2007-10-16 09:40
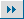
CHICAGO -- Julio and Mauricio Cabrera are gay brothers who are convinced their sexual orientation is as deeply rooted as their Mexican ancestry. They are among 1,000 pairs of gay brothers taking part in the largest study to date seeking genes that may influence whether people are gay.
 Julio Cabrera poses in a park near his home in Chicago on Aug. 20, 2007. Cabrera and his brother, Mauricio, from Olathe, Kan., are and are among 1,000 pairs of gay brothers nationwide who are donating blood or saliva to help scientists search for genetic clues about the origins of homosexuality. [Agencies] |
The Cabreras hope the findings will help silence critics who say homosexuality is an immoral choice.
If fresh evidence is found suggesting genes are involved, perhaps homosexuality will be viewed as no different than other genetic traits like height and hair color, said Julio, a student at DePaul University in Chicago.
Adds his brother, "I think it would help a lot of folks understand us better."
The federally funded study, led by Chicago-area researchers, will rely on blood or saliva samples to help scientists search for genetic clues to the origins of homosexuality. Parents and straight brothers also are being recruited.
While initial results aren't expected until next year -- and won't provide a final answer -- skeptics are already attacking the methods and disputing the presumed results.
Previous studies have shown that sexual orientation tends to cluster in families, though that doesn't prove genetics is involved. Extended families may share similar child-rearing practices, religion and other beliefs that could also influence sexual orientation.
Research involving identical twins, often used to study genetics since they share the same DNA, has had mixed results.
One widely cited study in the 1990s found that if one member of a pair of identical twins was gay, the other had a 52 percent chance of being gay. In contrast, the result for pairs of non-twin brothers, was 9 percent. A 2000 study of Australian identical twins found a much lower chance.
Dr. Alan Sanders of Evanston Northwestern Healthcare Research Institute, the lead researcher of the new study, said he suspects there isn't one so-called "gay gene."
It is more likely there are several genes that interact with nongenetic factors, including psychological and social influences, to determine sexual orientation, said Sanders, a psychiatrist.
Still, he said, "If there's one gene that makes a sizable contribution, we have a pretty good chance" of finding it.
Many gays fear that if gay genes are identified, it could result in discrimination, prenatal testing and even abortions to eliminate homosexuals, said Joel Ginsberg of the Gay and Lesbian Medical Association.
|
|
|
||
|
||
|
|
|
|