As mercury climbs in Europe, heatwaves may become norm
Updated: 2019-07-25 02:22
BRUSSELS/MADRID - Belgian zookeepers fed chickens in giant ice cubes to tigers on Wednesday as northern Europe baked in record temperatures during another heatwave that climate experts believe could become the new normal.
For the second time in a month, a high pressure system drew scorching air from the Sahara desert, breaking records for Belgium and the Netherlands, and threatening the same in Britain, Germany and France in a heatwave that is due to last until Friday.
In Spain, a wildfire in the northern province of Zaragoza was almost under control, but there was a risk of further outbreaks, especially in eastern parts, where the temperature was set to rise as high as 41 C .
Italian authorities issued fire alerts for the Mediterranean island of Sardinia, where temperatures were expected to climb above 40 C. They also put 13 cities on their highest "red" weather alert – warning of a possible health threat for everyone, not just the frail and infirm.
In Portugal, the largest wildfire so far this year, which raged over the weekend, was put out by more than 1,000 firefighters on Tuesday, but the country remained on high alert.
Further north, the temperature in Belgium struck 39.9 C, smashing the country's previous high of 36.6 C in June 1947 in records dating back to 1833, according to David Dehenauw, the head of forecasting at the Royal Meteorological Institute.
It was set to be even hotter on Thursday.
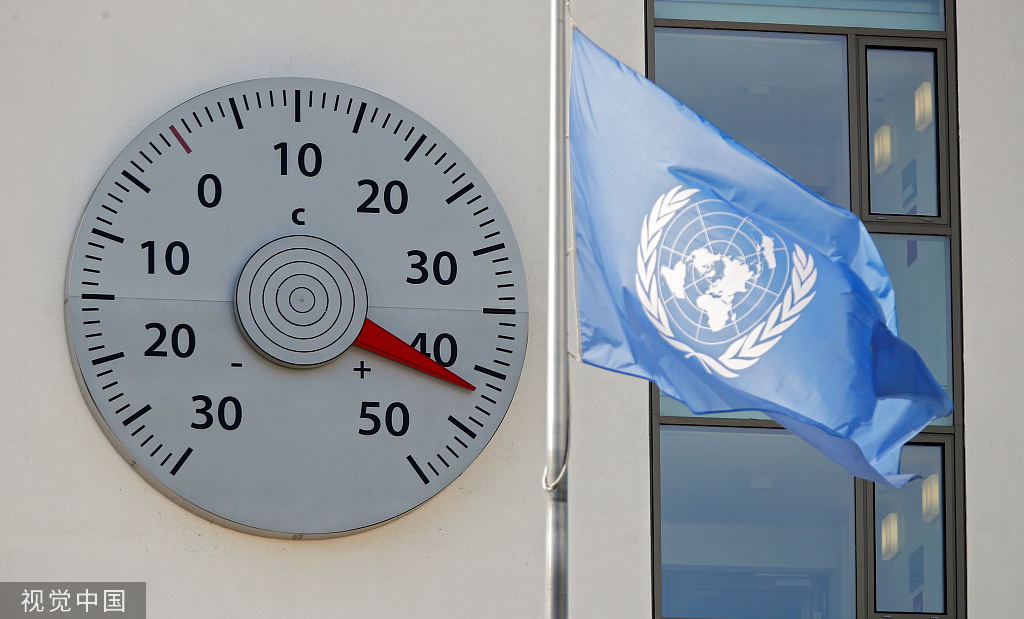

The institute had on Tuesday issued its first ever "code red" warning - a system it has used for 20 years - urging the public to drink plenty of water and keep out of the sun.
The temperature was set to exceed the local record of 40.4 C on Thursday in Paris, where the chief architect of rebuilding at the fire-ravaged Notre-Dame cathedral said the heatwave risked precipitating the collapse of the vaulted ceiling.
The Netherlands hit its own all-time high of 38.8 C, breaking a record dating from 1944.
Germany issued a heat warning for the entire country and said its own record of 40.3 C could be broken on Thursday.
Britain's Met Office forecast a record high for July of 38 C would be hit in southeast England.

HEATWAVES THE NORM
At Pairi Daiza, a zoo in western Belgium, keepers fed chickens inside giant ice cubes to their tigers and watermelons, also encased in ice, to their bears.
Visitors also received a free bottle of water.
"We made caves with air conditioning inside for pandas, as they are the most vulnerable to such hot weather, but they still prefer to stay outside, because they love the space," zoo spokesman Mathieu Goedefroy said.
Children on holiday frolicked in fountains, while adults swam and enjoyed ice cream.
"This is the nicest thing that could happen," said Munich resident Manuela Lukas. "It is sad the winter is so long and there are not so many beautiful days in Germany either, so you have to take advantage of it and just enjoy it."
However, climate specialists said such heatwaves are becoming more frequent as a result of global warming.
"With further climate change there could be a 50 percent chance of having hot summers in future. That's similar to saying that a normal summer in future will be as hot as our hottest summers to date," said Declan Finney, a research fellow at the University of Leeds in Britain.

DEADLY HEAT
Peter Innes, a senior climate research scientist at Britain's University of Reading, said the recent greater frequency of hot summers was in line with expectations about manmade global warming.
He referred to a study looking at the European heatwave of 2003 and a finding that by the middle of the 21st century, this could be the norm.
"It has been estimated that about 35,000 people died as a result of the European heatwave in 2003, so this is not a trivial issue," he said.
Bruneau Etienne, president of Belgian beekeeping federation CARI, said bees were under threat because at excessive temperatures, they preferred to stay inside hives, meaning they did not collect pollen and risked dehydration.
"If the situation continues, colonies of bees will die," he said.
Reuters
























