Diversification key to provinces' success
By Ed Zhang (China Daily) Updated: 2014-05-06 14:39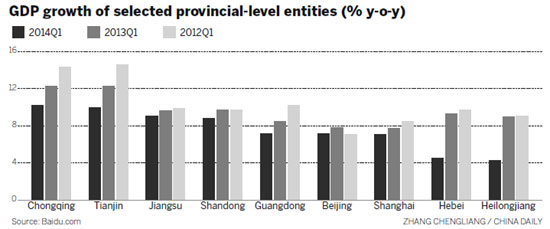
Geographically, China is large. But historically and economically, it used to be small. Ever since the 1100s, the country has been heavily dependent on business activity in one or several small areas for maintaining an imperial government.
An example of this is the grain stocks the central government needs to feed its officials, the army and distribute in areas that have been affected by natural disasters. People often used to say, without much exaggeration, that once Hunan and Hubei (two rice-producing provinces on the middle reaches of the Yangtze River) had reported a good harvest, supply was guaranteed to all under heaven.
 |
 |
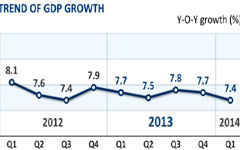
Of the 30 provincial-level entities in the mainland, Shanghai's ranking has slipped to eighth, while three coastal provinces Guangdong, Jiangsu and Shandong reported GDPs in excess of 1 trillion yuan during the first quarter, and with higher growth rates than Shanghai.
There is little doubt that modern China can draw financial resources from a much larger area than was historically the case. But it is the entire east coast that is generating most of the wealth. This change is good as it adds more diversity to the economy than one or two cities or provinces can. Here, diversity also means a regional economy's ability to connect with diverse resources within and without its geographic boundary.
Nonetheless, officials don't often realize the importance of business diversity and integration. There are a few provinces that remain dependent on just one or two industries. They have failed to develop their local business diversity as well as other provinces have.
- Diversification key to provinces' success
- Reform is a bright spot amid gloomy data from Q1
- Money market funds must come under controls
- Premier helps launch new expressway
- HED: Shenma search engine looks to take on Baidu
- Oil prices drop on weak Chinese manufacturing data
- China-Africa trade cooperation has broad prospects: Chinese minister
- Factors of various hues take gloss out of mall cosmetics
















