Private banks seek path to survive
(Xinhua) Updated: 2014-08-01 10:00SHANGHAI/HANGZHOU - Within six months, three banks set up by Chinese private entrepreneurs will open for business, raising questions as to how can they fit in a sector dominated by State-owned lenders.
China's banking regulator gave the go-ahead last week for several companies to set up the banks incorporated and run by domestic, private firms in three cities in East China, where economic output accounts for more than 60 percent of the country's total.
The pilot, which seeks to add five private lenders, is being implemented at a time when China is pushing for interest rate liberalization and more efficient allocation of credit.

|
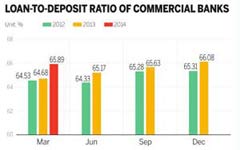
|
Yet this prospect does nothing to dishearten private entrepreneurs from making inroads into the banking industry. Interest and applications for joining the pilot program have already come from a diverse range of companies, from conglomerates such as the Shanghai-based Fosun Group to Internet behemoths Alibaba and Tencent.
However, bankers have urged caution, warning that failure of a bank would wreak havoc.
In terms of the pilot, authorities have taken a measured approach to prevent a reckless private bank opening binge.
There are also concerns about firms that apply to open a private bank and use it to secure cheap credit for themselves instead of lending to other companies based on creditworthiness.
Chen Xiaojun, Chairman of Taizhou Bank in East China's Zhejiang province, said that instead of approving new establishments, authorities should consider changing ownership structures of existing rural and urban commercial banks by replacing their government stakeholders with private ones.
Taizhou Bank underwent such a reshuffle in the early 2000s, with the local government now holding only a 5-percent stake in the bank.
Lian Ping, chief economist with Bank of Communications, China's fifth largest lender by assets, said the success of these up-and-coming lenders lies in their ability to meet demands in areas long ignored by large state banks.
- China credit card payments surge in 2013
- Chinese equity markets see best month since 2012
- China's July PMI rises to 2-yr peak
- Kela's changes aim to make a sparkle
- MIIT announces new capacity-cutting plan
- Alibaba's stake in Snapchat may buoy mobile portfolio
- Preparing for takeoff
- 146 imported food batches rejected in June















