China gaining ground in business influence
By Zhong Nan (China Daily) Updated: 2016-01-27 08:11
 |
|
Pakistani workers assemble photovoltaic cells at the Abubakar Jinnah Solar Industrial Park in Punjab province. The photovoltaic cell project has got an investment of $1.5 billion from ZTE Energy Co Ltd and will be completed in 2017.[Photo/Xinhua] |
China and Germany are becoming the strategic sources of new investment capital after the United States and the United Kingdom, a new survey said on Tuesday.
According to the 2015 annual investor relations survey conducted by global investment firm BNY Mellon, China moved up to the third place from fifth and Germany to fourth from seventh displacing Singapore and Japan in the process.
BNY Mellon is a depositary for more than 2,700 United States and global depositary receipt programs. The survey-Global Trends in Investor Relations-is in its 10th year. It is based on results from 550 respondents in 54 countries and regions, and covers sectors such as financials, industrials, consumer, technology and healthcare.
According to the survey, the top two concerns for respondents over the next five years are the systemic market and political risks. Uncertainty over new regulatory environments is now ranked fifth among the concerns, compared with a third ranking in the 2014 survey.
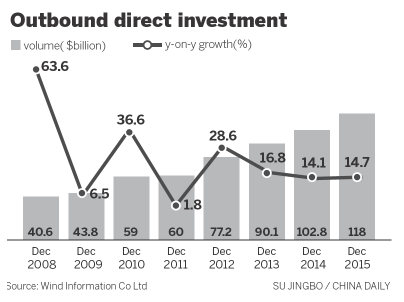
Yin Zonghua, vice-chairman of the China Council for the Promotion of International Trade, said the surge in China's outbound direct investment including merger and acquisition deals, as well as greenfield investment, can be attributed to a host of developments that have taken place both outside and inside China.
Within the country, a relaxed policy environment, abundant cash reserves and a rising private sector have spurred Chinese companies to learn from their foreign rivals and seek bargains overseas via M&As.
With China's business influence rising, a growing number of foreign companies in developed countries are keen to partner or work with Chinese companies.
On the five most important new sources of investment capital in the next five years, the survey's rankings as chosen by respondents are: the US (91 percent), the UK (76 percent), China (50 percent), Germany (45 percent) and Singapore (44 percent).
"China's ongoing structural changes are also taking place in the global economy, driven by market interests and policy supports, domestic companies have accelerated the pace of 'going global' to diversify global market channels through making outbound direct investment," said Feng Yaoxiang, CCPIT's spokesman.
CCPIT will publish the risk assessment report and legal guide on markets along the Belt and Road Initiative this year to assist and ensure its companies can safely provide financial services, infrastructure and manufacturing projects in these overseas markets.
The initiative, proposed by China in 2013, is a trade and infrastructure network that includes the Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road. The planned network connects Asia, Europe and Africa and passes through more than 60 countries and regions.
- Experts: Testing times ahead to attract investments
- China gaining ground in business influence
- Head of China National Statistics Bureau under probe
- Lufthansa signs deal with DJI in fledgling drone push
- Growing pains will pay off, say top economists
- Startups from China enjoy record year for financing
- Shares tumble to 13-month low amid rush to sell
- Slump in oil prices fuels increase in China's crude imports
















