Alibaba takes it to a whole new level
By Ed Zhang (China Daily) Updated: 2014-05-19 07:33Alibaba is a curious phenomenon. The Chinese e-commerce market-maker has recently announced plans to list its shares on the US stock markets, through a massive initial public offering, making it the largest tech IPO ever. Following that, in terms of market capitalization, it would perhaps find its place between Facebook and Walmart, as some analysts predict.
Few people can give a neat summary of the company's sprawling organization and all its interests in various sideline businesses. What they can say is only that there are many of them.
|
 |
|
 |
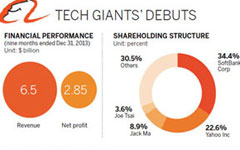
Those businesses generated a transaction volume of 1 trillion yuan ($160 billion) in 2012, more than the combined revenue of Amazon and eBay.
The key difference is that those businesses are not owned by Alibaba. The company is just the infrastructure and the service to facilitate their transactions, to make business easy, according to the company's mission statement.
Alibaba has two retail sites: Taobao, which features thousands of non-brand-name products sold by smaller merchants; and Tmall, which offers brand-name products. All merchants are subject to a user-generated open rating system based on the quality of their goods and delivery. It also has a site for customers to manage payments and other financial needs, which is not included in the listing plan.
The two retail sites are where shoppers must go to not only find goods that are not easily distributed in large batches or no longer available in large stores, but also to discover novelties. The size of their business is not the most important thing - though it is huge. Nor is the variety the two sites offer. What really makes Alibaba popular in China is its merchant rating system, in a country which still doesn't have a credit measurement standard for all the heavily indebted local governments or an open credit bureau whose data are shared by all financial services while remaining duly protected.
- Japanese investment in China requires cooperative efforts
- Fitch hails China's local govt bond decision
- WTO circulates report on US complaint over Chinese auto duties
- China voices reservations on WTO auto case ruling
- FTZ launches accounting unit for cross-border fund flow
- China to float 50-year T-bonds at 4.67% yield
- China's customs release pro-trade measures
- Shanghai GM to recall Buick vehicles