

If there is growth, there will always be growing pains. Trying to fit a large piece of furniture in a residential flat was one such pain. There could be so much trouble, as vividly recorded by our 1988 black-and-white photo, if the gate and stairway were so narrow that you had to haul in your newly acquired asset from the window.
Large pieces of furniture were important for a worker's family back then.
The National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) counted them along with bicycles and sewing machines as indicators of an urban family's level of consumer power.
While another kind of growth pain, albeit equally painful, is to wait humbly no matter what expensive vehicle you are in, for your turn to crawl your way out of a dense traffic jam like the one in the 2007 color photo on the fly-over near Guo Mao, one of Beijing's main business areas and the area with the largest number of modern buildings.
Public services are inadequate here and there, even in the largest cities in China. In fact, people often have to wait, with a much greater patience than they need to ride out a traffic jam, for their first telephone, first neighborhood medical clinic and automatic telling machine, first subway or expressway to connect their homes to workplaces, and many other conveniences and services.
Just from these two photos, people can all tell how the skylines of Chinese cities have changed. This year, to mark the 30th anniversary of the economic reform, many stories of great changes can be told of cities and of individuals' lives. But 30 years of change, however major and profound, is still part of a larger and longer process in which the nation learns to build and manage a modern society.
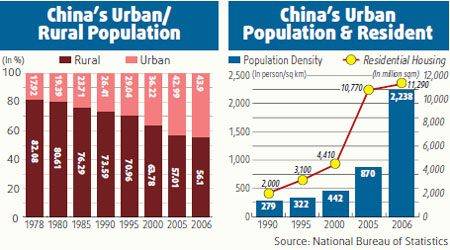
One major factor driving so much change and also giving rise to so much growth pain is the migration into the cities. When China was at the beginning of its economic reform, it was, except for a few cities, an agrarian society. More than 80 percent of its population was in the countryside.
Now, according to the NBS data, the size of urban population has grown nearly 150 percent and it will probably see as much growth in the next two or three decades.
Although fewer now need to hire a hoist to move furniture into an apartment, people will continue to press for, and at times also wait patiently, for the changes they want.

(China Daily 12/15/2008 page1)













