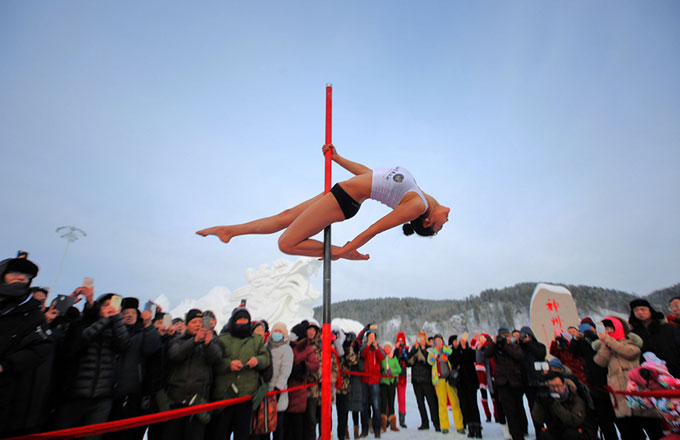
Major centers look for ways to cure 'big city disease'
|
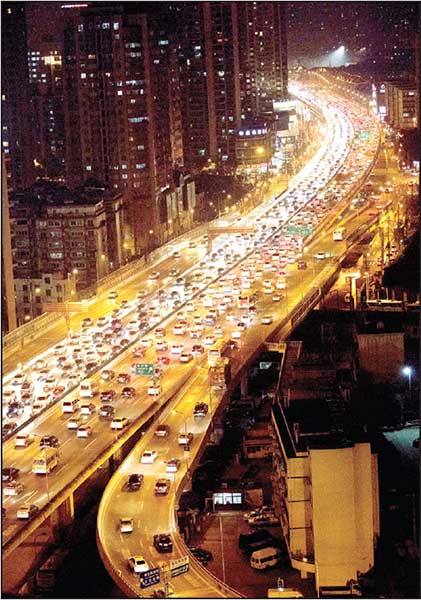
An overpass in Shanghai during the evening rush hour. The growing number of cars on China's roads is a major cause of air pollution in many cities.Zhang Guangyao / For Chinadaily |
Unbalanced urban and rural development is driving up the populations of China's largest cities and resulting in a lack of basic amenities and social services. Du Juan reports.
Editor's note: This is the last in a series of special reports looking at the effects of hukou, China's household registration system, on the lives of ordinary citizens who have left their homes to work in other areas and regions.
This week's pollution red alert in Beijing and many other large cities not only aroused public concern about air quality, but also drew attention to what has become known as "big city disease", a key urban issue the government has attempted to address in recent years.
This "disease" - environmental pollution, traffic congestion and a shortage of public services, including education and medical care - has been caused by the rapid rise in the populations of megacities such as Beijing and Shanghai.
In part, the problem is the result of the unbalanced allocation of resources between rural and urban centers, which has caused economic disparities and prompted people to rush to the largest cities in search of work, banking on more opportunities and fairer systems of resource allocation.
Every Chinese citizen must be registered with their local public security department at birth. However, there are two types of hukou, or household registration - rural and urban - which are accorded different rights. Traditionally it has been hard to change classification.
In October, the State Council, China's Cabinet, announced a plan to narrow the gap between urban and rural areas and promote better-balanced development by lifting the requirements on people with rural hukou who want to settle in cities.
The plan encourages rural people who are able to work and live without the aid of government subsidies to register in cities and change their hukou status to "urban".
The objective is clear: By the end of 2020, about 45 percent of the population should be living in urban areas, according to the central government. That will mean that during every year of the 13th Five-Year-Plan period (2016-2020) as many as 13 million rural households will have to become registered urban citizens.