History and forgetting
|
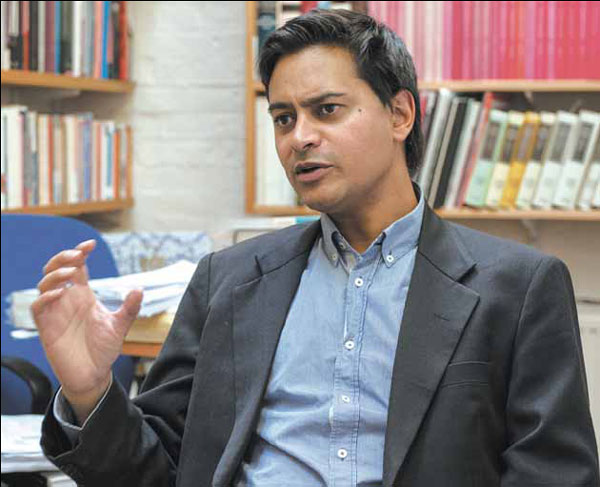
Oxford historian Rana Mitter draws on new material to talk about one of the great untold stories of the 20th century. Nick J. B. Moore / For China Daily |
The China theater of World War II is sometimes forgotten today in the West. But one historian aims to change that, Andrew Moody in Oxford reports.
Rana Mitter is determined to shed light on what is often seen in the West - although clearly not in China - as the forgotten war.
Despite killing up to 20 million people, including many savagely such as in the infamous Nanjing Massacre, and creating between 80 and 100 million refugees, China's War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression (1937-45) is often treated as a World War II sideshow.
"I thought it was one of the great untold stories of the 20th century and certainly the World War II period," he says.
"You can go into any history section in a bookshop and see endless books on Nazi Germany, the Blitz or the Americans in the Pacific war but it seemed to be that this story of a huge number of deaths, refugees and the destruction of the country that resulted in a huge change in the historical trajectory was often almost completely ignored," he says.
With China's War With Japan 1937-1945: The Struggle for Survival, which is the result of 10 years of extensive research and is seen as one of this year's most important books on China, the Oxford historian aims to redress that balance.
Mitter, who was speaking in the front room of his terraced home in Oxford on a rainy spring day after an overnight flight from Washington, says the present day low profile of the war in the West is in contrast to how it was seen at the time.
"People were concerned with the spread of world fascism and it attracted almost as much attention as the Spanish Civil War. English writers like Christopher Isherwood and W. H. Auden traveled to China to report on it. It was not seen as a local thing then," he says.
Mitter was awarded a $1.3 million award from the Leverhulme Trust, a major academic funding body in the United Kingdom, in 2004, and that has enabled him to fund a team of researchers around the world.
Far from being some Western history of the war, the book extensively uses material in the Chongqing Municipal Archive (from where China was governed for most of the war), the No 2 National Archive in Nanjing, Jiangsu province, as well as the National Archives at the University of Maryland, College Park, which has major sources on the US' China wartime experience.
The book also cites Kuomintang leader Chiang Kai-shek's diary at the Hoover Institution at Stanford University, which had been made available to scholars.