China-Russia drills a boon to mutual trust
 |
|
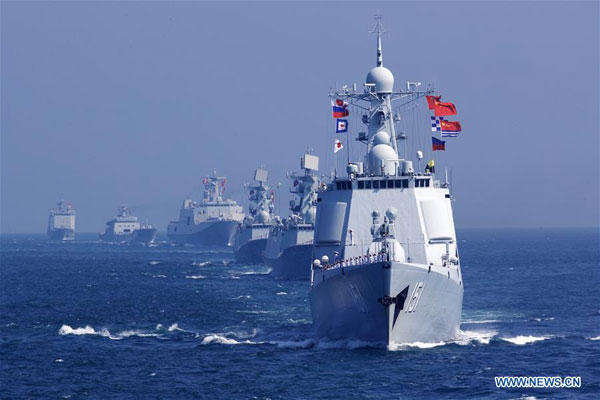
Chinese officers and soldiers waves to say goodbye to Russian fleet during a China-Russia naval joint drill at sea off south China's Guangdong province, Sept 19, 2016. [Photo/Xinhua] |
The navies of China and Russia started the second stage of their weeklong "Joint Sea-2017"military drills in the Sea of Japan on Monday, following the first stage which was held two months ago in the Baltic Sea. The drills, held annually since 2012, will for the first time reach the Sea of Okhotsk, north of Japan's Hokkaido Island, and involve joint submarine rescue missions and antisubmarine operations.
These "firsts" and the kickoff date, which is often linked to the September 18 Incident, have drawn speculations from some media outlets. On Sept 18, 1931, Japanese soldiers triggered a blast on a railway line in Northeast China, blamed the Chinese military for it and used it as a pretext for the invasion of China.
The truth, however, is, China's naval ambitions go beyond emotional links with a painful memory. The historical issues between Beijing and Tokyo are not likely to be settled by a naval drill in the neighborhood, nor do they have anything to do with "Chinese muscle-flexing". China and Japan can truly reconcile only when the latter faces up to the crimes it committed against the Chinese people before and during World War II.
The Chinese navy has good reason to go further offshore and work closely with its Russian counterpart. The Sea of Japan is not "Japan's Sea" but part of the wide ocean. From the Baltic Sea to the Sea of Okhotsk, the Chinese-Russian naval exercises are intrinsically about strengthening the strategic partnership between the two permanent members of the United Nations Security Council.
The two neighbors' regularized joint drills are more of a boon to mutual trust and regional order, and do not necessarily target a third party. Those who doubt this contention prefer to forget the fact that the United States holds a slew of annual military drills with its Asian allies in the region. It would be way too easy to point the same fingers toward Washington, which, of course, does not make much sense.
It may be fair to say that military drills have become a part of the standard practice in the Asia-Pacific, because of the escalating security tensions in the region. Traditionally known as a land power that didn't pay enough attention to its navy, China is catching up with leading naval powers rather rapidly, and to the discomfort of many countries.
A stronger navy has played a major role in protecting China's maritime interests and providing more public goods to the international community. Since 2008, it has dispatched 26 escort task force groups, including more than 70 ships to the Gulf of Aden and the coast of Somalia. And it has provided protection to more than 6,300 Chinese and foreign vessels during these missions. The Chinese-Russian naval cooperation, too, has gone beyond bilateral drills, as the two navies jointly escorted the Syrian chemical weapons in 2014.
China, now the world's largest trading country, has every reason to develop its naval power to safeguard its trade routes and overseas businesses. It might take some time for some countries to accept the peaceful rise of the Chinese navy, as well as the fact that China has no intention of "seeking revenge" on countries it used to be at war with or those that committed atrocities on its people.
The author is the deputy dean of the School of International and Public Affairs, Jilin University.