The not-so-dire future of work in the age of technology
 |
|
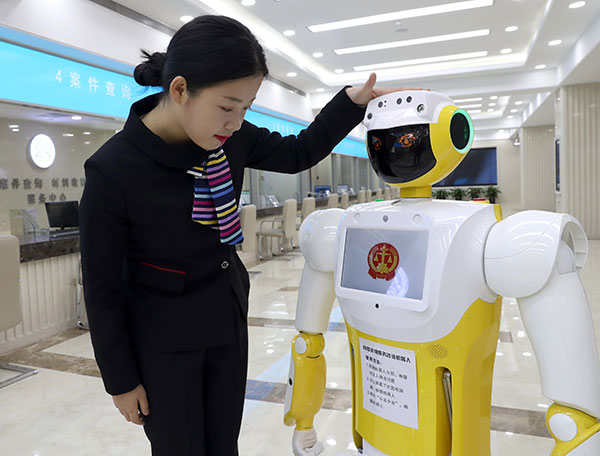
A staff member interacts with Xiaofa, a robot that provides simple legal advice and guidance for litigants, at Beijing No 1 Intermediate People's Court on Oct 12. [Zou Hong/China Daily] |
The future of work is a hot topic nowadays. It has inspired a seemingly endless train of analyses, commentaries and conferences, and it featured prominently in recent annual meetings of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank. For good reason: new technologies-digitization, robotics and artificial intelligence-have far-reaching implications for employment. But, contrary to how the story is often framed, a happy ending is possible.
The debate often skews toward the melodramatic, foretelling a future in which machines drive humans out of work. According to some bleak estimates, 47 percent of jobs are at risk in the United States; 57 percent in the OECD countries; two-thirds in developing economies; and half of all jobs globally (about 2 billion).
Similar dire predictions of large-scale job destruction and high tech-driven structural unemployment accompanied previous major episodes of automation, including by renowned economists. But technological change acted as a powerful driver of productivity and employment growth.
One key reason is that the technological innovations that destroy some existing jobs also create new ones. While new technologies reduce demand for low-to middle-skill workers in routine jobs, such as clerical work and repetitive production, they also raise demand for higher-skill workers in technical, creative and managerial fields. A recent analysis estimates that new tasks and job titles explain about half of the recent employment growth in the US.
Given this, the evolution of work should be viewed as a process of dynamic adjustment, not as a fundamentally destructive process that we should seek to slow. To erect barriers to innovation, such as taxes on robots, which some have proposed as a way to ease the pressure on workers, would be counterproductive. Instead, measures should focus on equipping workers with the higher-level skills that a changing labor market demands, and supporting workers during the adjustment process.
So far, education and training have been losing the race with technology. Shortages of the technical and higher-level skills demanded by new technologies are partly responsible for the paradox of booming technology and slowing productivity growth in advanced economies: the shortage of skills has constrained the diffusion of innovations. Imbalances between supply and demand have also fueled income inequality, by increasing the wage premiums that those with the right skills can command.
To address these shortcomings, education and training programs must be revamped and expanded. As the old career path of "learn, work, retire" gives way to one of continuous learning-a process reinforced by the aging of many economies' workforces-options for re-skilling and lifelong education must be scaled up.
This will demand innovations in the content, delivery, and financing of training, as well as new models for public-private partnerships. At the same time, countries must facilitate workers' ability to change jobs through reforms to their labor markets and social safety nets. This means shifting the focus from backward-looking labor-market policies, which seek to protect workers in existing jobs, to future-oriented measures, such as innovative insurance mechanisms and active labor-market policies.
Moreover, social contracts based on formal long-term employer-employee relationships will need to be overhauled, with benefits such as retirement and health care made more portable and adapted to evolving work arrangements, including the expanding "gig" economy.
On both of these fronts, France is setting a positive example. Early this year, the country launched a portable "personal activity account", which enables workers to accrue rights to training across multiple jobs, rather than accumulating such rights only within a specific position or company.
Technological change will continue to pose momentous challenges to labor markets across economies, just as it has in the past. But, with smart, forward-looking policies, we can meet those challenges head-on-and ensure that the future of work is a better job.
The author, a former director of development economics at the World Bank, is a non-resident senior fellow at the Brookings Institution.
Project Syndicate