Guardians of deadly vipers on China's Snake Island
China Daily | Updated: 2020-08-29 09:22
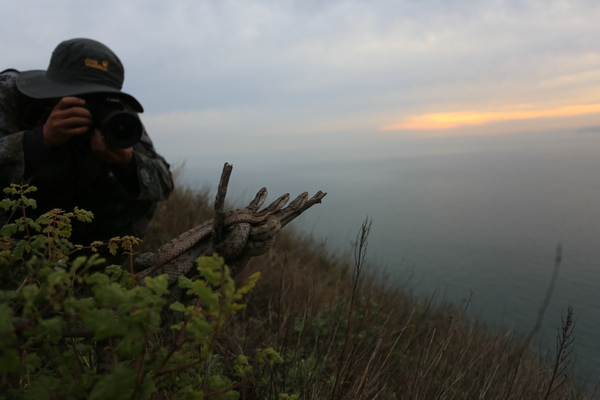

SHENYANG-Off the coast of the Liaodong Peninsula in the Bohai Sea, there lies a beautiful island with turquoise waters, luscious jungles and an incredible coastline. But few dare set foot on this idyllic isle due to the mysterious locals-around 20,000 native venomous snakes.
Sun Lixin, 61, is an exception. Sun and his colleagues have guarded Shedao Island or Snake Island for almost four decades, saving the Shedao Island pit viper (Gloydius shedaoensis), a species endemic to the island, from extinction.
Sun's efforts earned him the sobriquet "Snake Island Owner".
Battles among snakes, birds and humans
Shedao Island pit vipers have survived natural selection but only narrowly escaped extinction due to threats such as food scarcity, poaching and habitat loss over the past several decades.
Covering an area of 73 hectares, the island is around 10 km off the coast of Dalian, a city in Northeast China. As with other island serpents, the Shedao Island pit viper has developed a more potent venom in order to catch its main food source-migratory birds.
For generations, catching and eating birds had been a custom for local residents in the Laotie Mountain area, a stopover site for migratory birds near Snake Island.
"The pit viper's diet consists mainly of migratory birds. So the number of birds directly affects the population of snakes. They are in a biological chain," said Sun, former deputy director of Snake Island and the Laotie Mountain National Nature Reserve Administration.
Locals' fondness for medicinal liquor also posed a threat to the snakes. From the 1960s to the 1970s, the snake wine business was booming on the island, which led to rampant poaching.
"With its potent venom, a Shedao Island pit viper can kill a bird in five minutes. Some people believed that drinking snake wine could help cure disease, but there is no scientific basis to this. Nevertheless, these beliefs dealt a shattering blow to the snake population over the past century," said Wang Xiaoping, head of the administration's scientific research department.
After the People's Republic of China was founded in 1949, several surveys showed that there were 10,000 to 50,000 pit vipers on the island. In 1982, the number dropped to around 9,000, a record low. The venomous snakes were in imminent danger of extinction.
The snake species was listed as vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature's Red List of Threatened Species. In 1980, China set up a national nature reserve covering Snake Island and the Laotie Mountain area to protect the unique pit vipers, migratory birds and surrounding environment.