Blood donation rates stay steady despite pandemic
By Wang Xiaoyu | chinadaily.com.cn | Updated: 2021-06-10 17:28
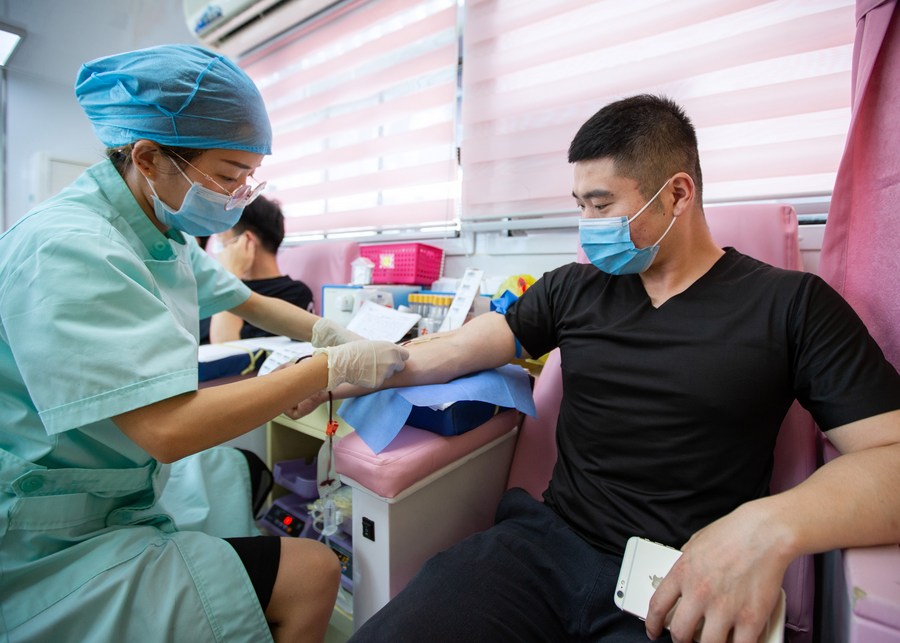
China's blood donations and overall supply have remained steady during the COVID-19 epidemic, the National Health Commission said on Thursday.
Guo Yanhong, an official with the commission's medical supervision and administration bureau, said more than 15.5 million blood donations were acquired last year, and the total amount of donated blood last year was 5,272 metric tons, slightly down by 0.48 percent from 2019.
"Due to movement restrictions imposed during the height of the pandemic last year, roadside blood collections were once affected, but many voluntary blood donors answered the call by masking on and going outside to donate their blood," she said, "Staff members at blood centers have also manned their positions to ensure a safe and stable blood supply."
Additionally, more than 4,700 convalescent plasma donations from recovered COVID-19 patients have been acquired, totaling about 1.47 million milliliters, according to the commission.
China established a system for clinical use of blood donations since 1998, when the blood donation rate stood at 4.8 per 1,000 people. Last year, the rate rose to 11.1 per 1,000 people, the commission said.
This year, the number of blood donations from January to April reached nearly 5.2 million, up 4 percent from the same period in 2019, the commission said.
Guo said a country's blood stock is deemed to be at a safe level if there is sufficient blood for seven days.
"Since July, the average blood stock nationwide can last at least 12 days," she said.
"As the summer holiday and flooding season are approaching, the traditional off-seasons for blood donations, we call on more healthy citizens to actively make donations during this time of the year," she said.
Guo added the commission will also step up monitoring and allocation of blood supply to better secure sufficient blood for clinical treatment.
























