1. Unique location:
 |
Jinjiang sits along the coast of Southeast Fujian, 5.3 miles from Taiwan’s Kinmen Island, faces the Western Taiwan Straits Economic Zone and is a bridgehead of cross-Straits cooperation.
2. Powerful economy:
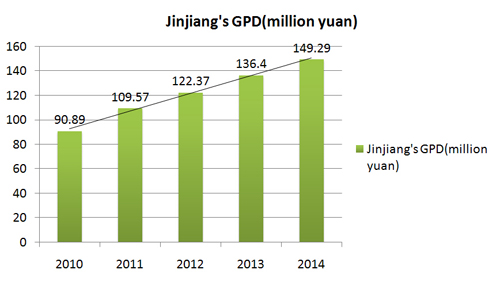
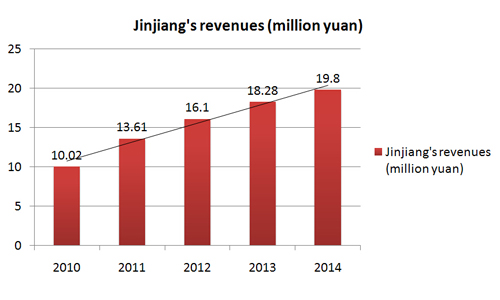
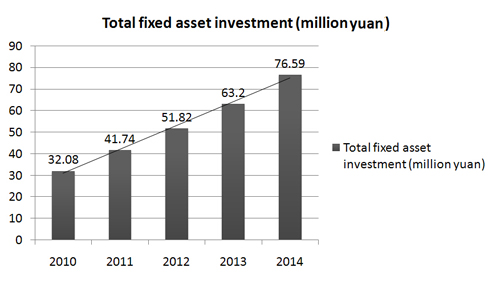
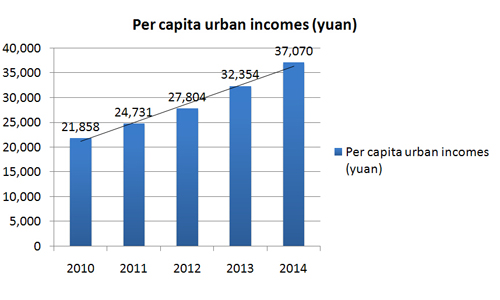
It ranks 5th among Chinese cities of its size in economic competitiveness and has more than 16,000 companies. In 2014, it had a GDP of 149.29 billion yuan and industrial output of 329 billion yuan, with revenues of 19.8 billion, total fixed asset investment of 76.59 billion, and per capita urban incomes of 37,070 yuan.
3. Convenient transport:
 |
This area is between the Pearl River Delta, Yangtze River Delta, and Taiwan Island, giving it sea, land and air transportation advantages. The Quanzhou International Airport has 23 flights reaching all parts of the country, including Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan and international lines to Korea, Thailand, and the Philippines.
The city’s ports at Weitou and Shenhu national ports, with the first handling container freight to Taiwan and Southeast Asia, and all major ports along China’s coast and the Yangtze River, while Shenhu has lines to Singapore, Russia, Indonesia, Republic of Korea, Japan and the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Also, the Quanzhou-Sanming and Shenyang-Haikou expressways pass through the city, and its ring expressway is now in use, and the Xiamen-Zhangzhou-Quanzhou expressway is in the planning stage.
The Fuzhou-Xiamen High-speed Railway passes through the city with a freight station that connects it with the cities of Ningbo, Nanjing, Shanghai and Shenzhen. It has a total of 2,383 kilometers of roads on a 370-sq-km area.
4. Facilities:
 |
It has 46 500-kV, 220-kV and 110-kV and LNG power stations, as well as thermal power stations, and trash-burning stations that generate 1.3-billion kWh annually, at a price of 0.65-yuan/kWh.
It has 28 reservoirs and 13 water plants providing 758,000 tons of water a day, covering every corner of the city, at a cost of 1.8 yuan/t.
It has more than 100-km of LNG pipelines carrying 240 million cubic meters of gas a year, costing 3.1 - 4.2-yuan/cu-m.
It also has five sewage treatment plants handling 185,000 tons of sewage every day at a cost of 1.1-yuan per ton, and one waste treatment plant and 37 waste transfer stations that process 535,000 tons of rubbish a year 100 percent at a cost of 4 yuan per capita.
5. Talented personnel:
 |
The city has a strategy of strengthening itself through talent and places priority on attracting talented personnel so that it now has 250,000 professionals that cover a range of fields. It has China’s first county-level post-doc station which has brought in at least 4,000 top people, including 75 post-docs, and an expert activity center and PhD association with 240 members.
It has subsidies and preferential policies for housing, start-ups, research, residence permits, family employment, education for children, and social insurance.