For a Life of Contentment
-The Rationale for China's Human Rights Development
China Daily | Updated: 2022-12-06 07:26
Chapter II
The Rationale: Living a Life of Contentment is the Ultimate Human Right
"Living a life of contentment is the ultimate human right." — This is the essence of China's rationale for human rights development. The people-centered concept of human rights defines the value China pursues in its human rights cause, and shows that putting emphasis on the people is the distinguishing feature of the Chinese path of human rights protection.

This concept includes four dimensions. In terms of the subject of human rights, it makes clear that the people are participants, promoters and ultimate beneficiaries of the cause of human rights. Human rights are not privileges enjoyed by a certain group or by just a few people, but inclusive rights enjoyed by the broad masses of the people; In terms of the connotation of human rights, the direction and focus of human rights development are set in line with the needs of the people. Human rights are expanded from the rights to subsistence and development to other aspects, and the people's aspiration for a better life is the goal of the human rights cause; In terms of human rights protection, whole-process people's democracy is implemented, which gives full play to the enthusiasm, initiative and creativity of the people, so that the people are relied on to drive the progress and development of human rights; In terms of the pursuit of values, the well-rounded development of the individual is taken as the supreme goal of human rights and living a life of contentment is regarded as the ultimate human right. The people's interests are constantly safeguarded and their sense of gain, happiness and security continuously enhanced.
2.1 The core philosophy, the principle of democracy, and the focus on people's livelihoods
The core philosophy — to remain committed to being people-centered. China's human rights cause takes safeguarding fundamental interests of the people as its starting point and ultimate goal. It is committed to serving, relying on, benefiting and protecting the people. Putting people first, upholding the principal position of the people, and putting the interests of the people above all else are the fundamental features of China's human rights development.
The principle of democracy — to remain committed to people being masters of their own country. Democratic rights are the basic human rights. In accordance with China's Constitution and laws, the people manage state and social affairs, economic and cultural undertakings and become masters of the country, society and their own destiny through the system of people's congresses, the system of CPC-led multiparty cooperation and political consultation, the system of regional ethnic autonomy and the system of community-level self-governance. This is the core essence of Chinese-style democracy.

The focus on people's livelihoods — to remain committed to people's wellbeing as the foundation of human rights development. To make sure that people live a good life, and enjoy better education, more stable employment, more satisfactory incomes, more reliable social security, higher-level medical and health services, more comfortable housing, a more beautiful environment and a richer cultural and spiritual life, make everyone free from fear and threat, and let everyone better develop themselves and live a happy life, these are the essence of people fully enjoying more human rights, giving new meaning to progress in human rights.
2.2 The theoretical rationale
From an epistemological point of view, human rights are historical, concrete and realistic. Human rights are the product of certain economic, social and historical conditions, and they develop with the changes of historical conditions. In this sense, the content and level of human rights protection are constantly enriched and improved. There is no end to improving human rights. There is no fixed model of human rights protection in the world. Different countries have different national conditions, histories, cultures, social systems and economic and social development levels. A proper path of human rights development should be explored to suit national conditions and the needs of the people.
From a practical point of view, human rights are promoted through development. Subsistence is the foundation for enjoying all human rights, and development is a must to guarantee subsistence and a foundation for the fulfillment of all other rights. Poverty is the greatest obstacle to human rights, and it must be shaken off through promoting economic development and social progress, so that common prosperity and well-rounded development are gradually achieved. This is China's key approach to advancing human rights protection.
From a dialectical point of view, human rights are the integration of individual and collective rights. There is no collective progress without individual development, while individuals can only enjoy well-rounded development in a collective context. Individual and collective human rights must be integrated and progress side by side, in order to achieve optimal development of human rights.
2.3 The objective, law-based governance, and the evaluation criteria
The objective — promoting the free and well-rounded development of individuals. It is the common pursuit of humanity to realize human rights for all. All people should enjoy full, comprehensive and high-level human rights, so that the free and all-round development of every individual can be ultimately realized, and everyone can fulfill self-development themselves and contribute to the society with dignity.
The roadmap marked by rule of law — upholding social fairness and justice. The principle of equity and justice is the eternal theme of the development of human society. Through improving the socialist institutional frameworks with Chinese characteristics and steadfastly advancing law-based governance, China has integrated the practice of respecting and protecting human rights into the whole process of legislation, law enforcement, administration of justice, and observance of the law, to ensure equal rights, equal opportunities and fair rules for all.
The evaluation criteria — people's sense of gain, of happiness, and of security. Human rights are not an ornament to be used for decoration. The people are the creators of history, and the builders and the fundamental force to rely on in the human rights cause. A country's human rights are essentially gauged by its own people. Whether the people's interests are safeguarded and whether their sense of gain, happiness and security is enhanced are important criteria for evaluating a country's human rights situation.
2.4 Global vision
In the wake of economic globalization and international challenges such as climate change and transnational infectious diseases, the Cold War mentality as well as the hegemonic practices of putting one's own country's interests above the interests of others and even the international community at large, and pointing fingers at other countries are not welcome. The democratization of international relations and the reinforcement of interdependence of the international community is an objective trend. [Liu Huawen, "Understanding the Communist Party of China's view of human rights," the Global Times, July 29, 2022]
The Chinese nation has always held these beliefs dear: "All people under the heaven are of one family" "All the people are my brothers and I share the life of all creatures" and "All nations should live in harmony." China's outlook on human rights has deep cultural roots, advocating that "a just cause should be pursued for the common good," which not only guarantees the human rights of the Chinese people, but also strives to pass down the spirit of benevolence and pursue one's own development as well as development for all. The Chinese people are ready to work with people all over the world to uphold the common values of peace, development, fairness, justice, democracy and freedom for all mankind, and to safeguard human dignity and rights.
On the path of human rights development, China is committed to replacing estrangement between civilizations with exchanges, clashes with mutual learning, and superiority with co-existence. China advocates dialogue and cooperation based on equality and mutual respect, and seeks to promote progress through cooperation and to ensure human rights with benefits deriving from development, so as to promote the healthy development of the global human rights cause.
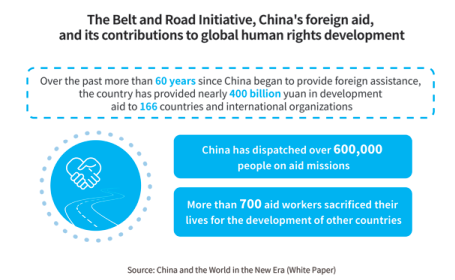
China firmly upholds the international system with the United Nations (UN) at its core and the international order based on international law, vigorously conducts South-South cooperation under the framework of multilateralism, and works toward the formation of a fairer, more equitable, reasonable and inclusive global human rights governance system. The notion of building a human community with a shared future has been written into many UN documents. The ideas including jointly building the Belt and Road and jointly building a global community of health for all as well as a community of life for man and Nature, and the initiatives including the Global Development Initiative and the Global Security Initiative, have all contributed to the cause of global human rights development, and have greatly enriched and developed the concept of human rights.