 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Providing funds for the future may be a problem, report Li Jing and Chen Jia in Beijing.
China's rapidly aging population is a ticking time bomb. Not only in terms of a predicted decline in the numbers of people available for work, but, equally importantly, in paying the vast pensions bill.
A census carried out in 2010 showed that the number of people aged 60, the official retirement age, or older was 177.6 million, accounting for 13.26 percent of the population. That figure is projected to exceed 200 million in 2014.
 |
In 2011, the national average monthly pension for the retired reached 1,500 yuan ($238), according to Finance Minister Xie Xuren, but pension levels vary according to the region in which the recipient lives.
For example, Beijing has said it will soon increase the average pension to about 2,510 yuan per month, while Urumqi, the capital city of the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, has this year set a target of raising its average pension to a monthly 1,900 yuan and the Ningxia Hui autonomous region will pay pensioners 1,785 yuan.
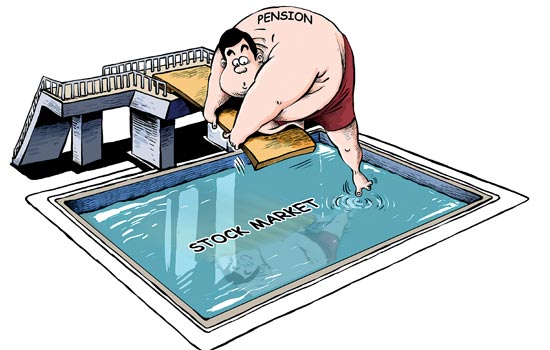
In response to the problem, China has just taken the first steps in reforming the way it manages the massive pension fund by beginning a trial investment in the country's stock market, in a move aimed at better preserving the value of the funds and supporting the country's aging population.
Last week, the southern province of Guangdong won approval from the State Council to entrust 100 billion yuan of its pension fund to the National Council for Social Security Fund for two years. The NCSSF said that most of the money would be placed in savings accounts or used to buy government and corporate bonds and other fixed-income securities. These financial vehicles may not be the most exciting on the planet, but they do have the advantage of security, and safety is the major priority for those operating the nation's pension fund.
Last week, the China Securities Journal reported that as much as 30 billion yuan of those funds is likely to be invested in the nation's equity markets. The council's rules forbid it from putting more than 40 percent of its total fund into equity investments.
The move comes against a backdrop of heated debate, lasting several months, over the wisdom of entrusting the nation's retirement funds to the volatile market, with critics arguing that the stock market needs urgent reform before such huge sums are invested.
Previously, most of Guangdong's 441 billion yuan pension fund was held in low-yield savings accounts, according to Ding Sanbao, chief accountant of the Guangdong provincial social security fund.
"As a result, the rate of return during the past five years has been just 2 percent," Ding was quoted as saying in the 21st Century Business Herald. "With the NCSSF managing the 100 billion yuan fund, we hope to increase that rate to about 4 percent," he said.
Nationally, the management of the pension fund, which totaled 1.92 trillion yuan in 2011, is not in good shape. Zheng Bingwen, head of the Global Pension Fund Research Center at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, also estimated that the rate of return during the past decade has been about 2 percent, the lowest in the world.
"In 2011, the nominal yield rate of the pension fund was less than 2 percent, but at the same time the country's consumer price index rose by 5.4 percent. So in real terms, the fund actually suffered a loss of nearly 100 billion yuan last year," said Zheng.
Since the beginning of the year, the China Securities Regulatory Commission, the country's top securities watchdog, has expressed a desire to absorb this huge pension pot into the stock pool. Analysts say that the move would likely boost investor confidence and could help the A-share composite indexes rise to bull-market levels, but the proposition has also prompted accusations that the CSRC has an ulterior motive and is merely intent on "saving the market".
The commission's chairman, Guo Shuqing, has strenuously refuted the accusations saying, "The capital market will (also) help to maintain and increase the value of the pension fund, which would protect the interests of investors."
However, the poor performance of China's share market in 2011, when the Shanghai Composite Index declined by 21 percent, the third-biggest fall in its 21-year history, has raised investor concerns about the security of the pension fund if it were to be invested in equities.
Li Qingyun, a professor at the School of Economics at Peking University, has expressed concern about the pension fund being invested in the opaque domestic stock market. "Because of the lack of transparency, there are many instances of illegality, such as market manipulation or insider trading," he said. "Would we be too hasty in putting our lifeline into a stock market such as this?"
Moreover, the immature issuing process for initial public offerings, combined with ineffectual regulation, has provided opportunities for some companies with unsound finances to "circle money", a situation where speculative capital chases high prices on IPOs and shares of non-profitable companies, which can cause wide market fluctuations and result in big losses for ordinary investors.
The situation led the Chinese economics commentator Wang Fuzhong to warn that the CSRC should not risk the pension fund simply to make the domestic stock market look better.